- Home
- Gezondheidsproblemen
- Cholesterol
- Berberine



Op voorraad
Berberine
Voedingssupplement met berberine: bloedsuiker, cholesterol, darmen...
- Berberine HCL: een 97% zuiver extract van berberis voor een gezond hart en bloedvatenstelsel.
- 100% natuurlijke oorsprong.
- Gegarandeerd zonder toevoegingen.
- 97% puur (hoogste percentage dat verkrijgbaar is).
- Product met een traditioneel gebruik (ayurvedische geneeskunst) met enorm potentieel.
- Draagt bij aan de gezondheid van maag-darmstelsel en hart- en bloedvaten.
Berberine
Vul uw selectie aan
Berberine 500 mg is een voedingssupplement van superieure kwaliteit op basis van zuurbes. Het bevat een uitzonderlijke hoeveelheid berberine, een fytonutriënt dat bekend staat om zijn opmerkelijke invloed op de gezondheid van hart- en bloedvaten. Het wordt al eeuwenlang gebruikt in de ayurvedische geneeskunst.
Wat is berberine?
Berberine is een plantaardige stof die aangemaakt wordt door bepaalde planten, waaronder de zuurbes (Berberis vulgaris). Berberine is een alkaloïde, oftewel een 'natuurlijk organisch bestanddeel met een complexe moleculaire structuur (heterocyclische verbinding) dat zelfs in zeer lage doseringen over uitgesproken fysiologische eigenschappen beschikt", aldus de uitgebreide definitie van de auteurs Winterstein en Trier. Het gaat hierom een groep fascinerende natuurlijke producten met een groot therapeutisch potentieel.
In vitro is deze alkaloïde stof in staat verschillende antioxidatieve, ontstekingsremmende, bloedsuikerverlagende, bloeddrukverlagende en lipidenverlagende effecten uit te oefenen (1 - 2). De belangrijkste eigenschap van de stof is echter dat het bijdraagt aan de blokkering van de calciumkanalen.
Waar vinden we berberine? We vinden berberine ook in de stekelpapaver, de goudzegel, de mahonie, de poelruit en de Berberis aristata, een struik die oorspronkelijk uit de Himalaya in India komt.
Hoe werkt berberine ?
Naar de werking en de effecten van berberine is veel onderzoek gedaan. De plant waaruit berberine wordt gewonnen wordt al eeuwenlang gebruikt in de traditionele geneeskunst: op kleitabletten van de persoonlijke bibliotheek van de Assyrische keizer Asurbanipal, daterend van 650 voor Christus is reeds bewijs gevonden voor het gebruik van Berberis vulgaris als middel om het 'bloed te zuiveren'. In de Ayurveda werd de plant ook wel gebruikt om verschillende infecties te behandelen, wonden te helpen genezen en 'de geest te openen'.
Er zijn wel vragen over de biologische beschikbaarheid wanneer men het oraal inneemt, want die zou relatief laag zijn. De absorptie in de darmen wordt ingeschat op 0,4% (6) tot 1% (7). In in vivo-studies is echter aangetoond dat het berberinegehalte in de weefsels na orale inname veel groter is dan het gehalte in het bloed. Het wordt snel verdeeld richting de nieren, de spieren, het hart, de alvleesklier, de vetten en de lever, waar het afgebroken wordt en omgezet in berberrubine, thalifendine en jatrorrhizine, de belangrijkste werkzame stoffen (8).
De werkingsmechanismen worden nog onderzocht: er verschijnen jaarlijks onderzoeken waarin de gunstige effecten worden beoordeeld voor het hart- en vaatstelsel.
Men heeft reeds farmacokinetische interacties geobserveerd bij het de gelijktijdige toediening van ciclosporine A (gebruikt voor de behandeling van auto-immuunziektes), en van metformine (een antidiabetesmedicijn dat gebruikt wordt voor de behandeling van diabetes 2 om de insulineresistentie van het lichaam te verminderen).
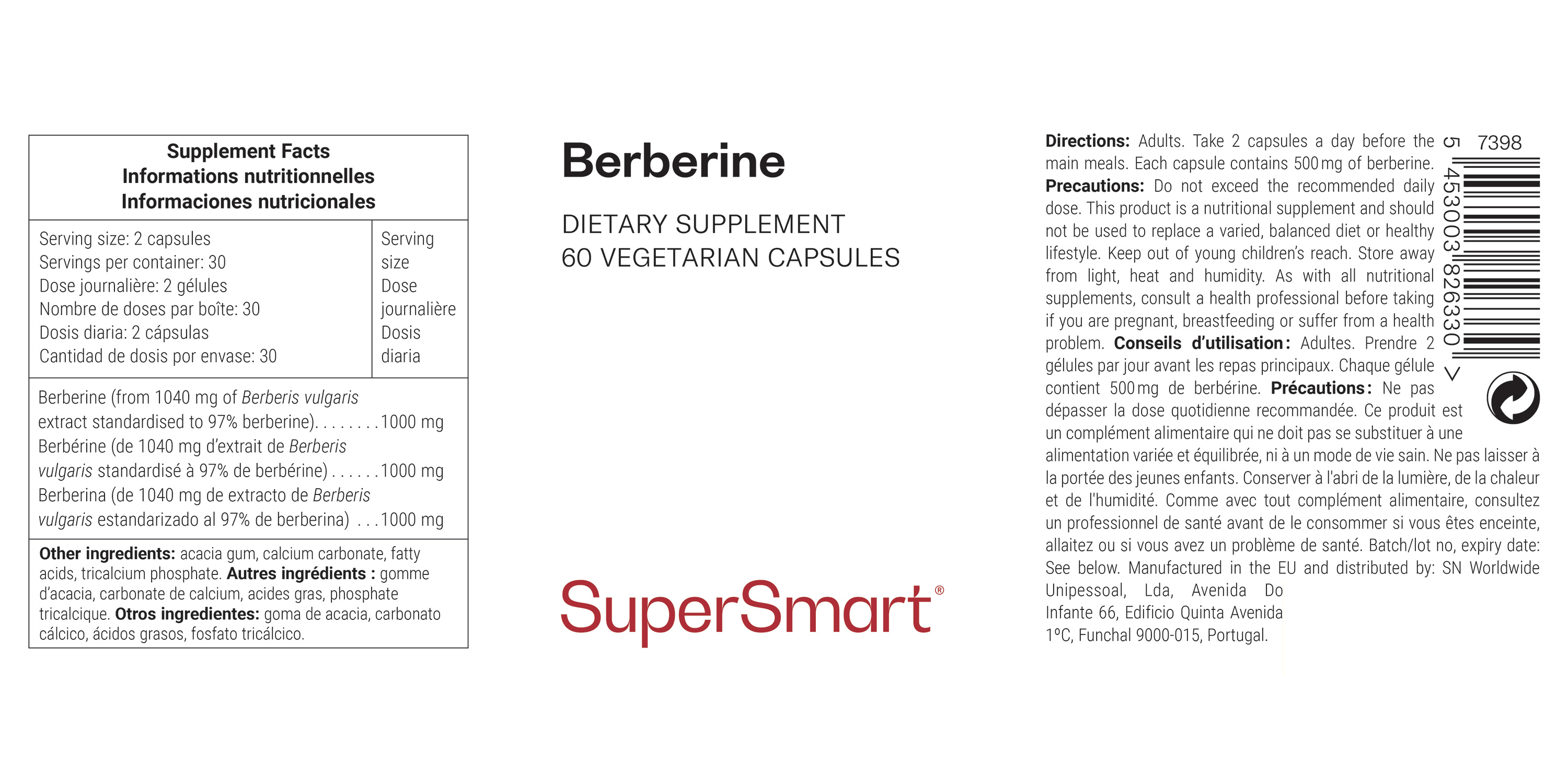
| Dagelijkse dosering: 2 capsules Aantal doses per potje: 30 |
Hoeveelheid per dosis |
| Berberine (van 1040 mg Berberis vulgarisextract gestandaardiseerd met 97% berberine) | 1 000 mg |
| Overige ingrediënten: Acaciagom, calciumcarbonaat, vetzuren, tricalciumfosfaat. | |
Elke capsule bevat 500 mg berberine.
- Mokhber-Dezfuli N, Saeidnia S, Gohari AR, Kurepaz-Mahmoodabadi M. Phytochemistry and pharmacology of berberis species. Pharmacogn Rev. 2014;8:8.
- Bhardwaj D, Kaushik N. Phytochemical and pharmacological studies in genus Berberis. Phytochem Rev. 2012;11:523–542
- Mazandarani M, Ghasemi N, Bayat H. The second review and comparison of active ingredients in plant organs of Berberis vulgaris L. J Plant Sci Res. 2013;8:59–17.
- Madiseh MR, Heidarian E, Rafieian-kopaei M. Biochemical components of Berberis lycium fruit and its effects on lipid profile in diabetic rats. J HerbMed Pharmacol. 2014;3:1.
- Kermanshahi H, Riasi A. Effect of dietary dried Berberis vulgaris fruit and enzyme on some blood parameters of laying hens fed wheat-soybean based diets. Int J Poult Sci. 2006;5:89–93.
- Liu YT, Hao HP, Xie HG, et al. 2010. Extensive intestinal first-pass elimination and predominant hepatic distribution of berberine explain its low plasma levels in rats. Drug Metab Dispos 38: 1779–1784.
- Chen W, Miao YQ, Fan DJ, et al. 2011. Bioavailability study of berberine and the enhancing effects of TPGS on intestinal absorption in rats. AAPS PharmSciTech 12: 705–711
- Tan XS, Ma JY, Feng R, et al. 2013. Tissue distribution of berberine and its metabolites after oral administration in rats. PLoS One 8: e77969.
- Imenshahidi M, Hosseinzadeh H. Berberis Vulgaris and berberine:an update review. Phytother Res. 2016;30:1745–1764.
- EFSA opinion reference 2010;8(10):1734
- EFSA opinion reference 2010;8(10):1747
- EFSA opinion reference 2011;9(6):2207
- Feng R, Shou JW, Zhao ZX, He CY, Ma C, Huang M, et al. Transforming berberine into its intestine-absorbable form by the gut microbiota. Sci Rep. 2015;5:12155.
- Chang, W., Zhang, M., Li, J., Meng, Z., Wei, S., Du, H., et al. 2013. Berberine improves insulin resistance in cardiomyocytes via activation of 5=-adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase. Metabolism, 62(8): 1159–1167. doi: 10.1016/j.metabol.2013.02.007. PMID:23537779
- Yun S. Lee, Woo S. Kim,Kang H. Kim, Myung J. Yoon, Hye J. Cho, Yun Shen, Ji-Ming Ye, Chul H. Lee, Won K. Oh, Chul T. Kim, Cordula Hohnen-Behrens, Alison Gosby, Edward W. Kraegen, David E. James, and Jae B. Kim, Berberine, a natural plant product, activates AMP-activated protein kinase with beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic and insulin resistant states, Diabetes, 2006.
- Hu, Y., and Davies, G.E. 2010. Berberine inhibits adipogenesis in high-fat dietinduced obesity mice. Fitoterapia, 81(5): 358–366. doi:10.1016/j.fitote.2009.10. 010. PMID:19861153.
- Zhang, M., Lv, X., Li, J., Meng, Z., Wang, Q., Chang, W., et al. 2012. Sodium caprate augments the hypoglycemic effect of berberine via AMPK in inhibiting hepatic gluconeogenesis. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 363(1–2): 122–130. doi:10.1016/j. mce.2012.08.006. PMID:22922125.
- Ko, B.S., Choi, S.B., Park, S.K., Jang, J.S., Kim, Y.E., and Park, S. 2005. Insulin sensitizing and insulinotropic action of berberine from Cortidis rhizoma. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 28(8): 1431–1437. doi:10.1248/bpb.28.1431. PMID:16079488.
- Chang, W., Chen, L., & Hatch, G. M. (2015). Berberine as a therapy for type 2 diabetes and its complications: From mechanism of action to clinical studies. Biochemistry and Cell Biology, 93(5), 479–486. doi:10.1139/bcb-2014-0107.
Waaruit bestaat Berberine
Vragen? Bedenkingen?
Ons team van voedingsdeskundigen en wetenschappers heeft de antwoorden.
De plantenfamilie van de Berberis komt overal ter wereld in subtropische gebieden voor. Zo komt het ook dat het in verschillende traditionele geneeswijzen algemeen gebruikt wordt, zoals in de ayurvedische geneeskunst en de Chinese geneeskunst.
Ons berberinesupplement is afkomstig van de Berberis vulgaris (zuurbes) die voornamelijk voorkomt in Iran. Dit land is met zijn 11.000 hectares aan zuurbesteelt dan ook de grootste producent ter wereld. Verschillende onderdelen van de plant hebben een grote therapeutische waarde, zoals de schors, de wortel en de takken. Maar de gedroogde vruchten worden het meest gebruikt (3 - 4). Het is beoordeeld als veilig voor menselijke consumptie en het is bevestigd door de Amerikaanse FDA (5).
In de zuurbes zitten nog andere alkaloïden, zoals oxyaconthine, berbamine, brociline en columbamine, maar wetenschappers zijn het meest geïnteresseerd in berberine.Dat is de reden waarom we het natuurlijke extract hebben verrijkt met berberine (gegarandeerd gehalte van 97% aan werkstoffen).
Wie te hoge bloedsuikerwaarden wil tegengaan en de gezondheid van hart- en bloedvaten wil verbeteren, is wellicht ook geïnteresseerd in ander voedingssupplementen.
- DHA (docosahexaeenzuur), dat als supplement wordt verkocht onder de naam Super DHA draagt bij aan het behoud van normale triglyceridewaarden (10).
- PectaSol® (een natuurlijk concentraat van pectines uit citroen) draagt bij aan de beperking van de stijging van de bloedsuikerspiegel na de maaltijd (wanneer het tijdens de maaltijd wordt ingenomen in een dosis van minimaal 10 g) (11).
- Beta 1.3/1.6 Glucan, een natuurlijke stof uit de celwand van een gistvorm, draagt bij aan het behoud van een optimale cholesterolwaarde in het bloed (12).
Kiest u liever iets op het gebied van de fytonutriënten, dan heeft u ook voldoende interessante alternatieven:
- Apple Polyphenols, een concentraat van polyfenolen uit appel.
- Een broccoli-extract dat gestandaardiseerd is m et sulforafaan en glucosinaat.
- Olive Leaf Extract, een mediterrane formule met drievoudige werking tegen cholesterol en triglyceriden in het bloed;
- Double Pomegranate, een supplement met een sterke antioxidatieve werking op basis van granaatappel.
De capsules van dit product zijn samengesteld uit pullulan, een natuurlijke polysacharide afkomstig uit de fermentatie van tapioca of maïs. Pullulan bevat geen ingrediënten van dierlijke oorsprong en biedt een uitstekende barrière tegen zuurstof, wat helpt om de integriteit van de ingrediënten in de capsule te behouden. Het biedt ook een uitstekend milieuvriendelijk alternatief voor synthetische materialen.
Het extract vanBerberis vulgaris dat SuperSmart u biedt is gestandaardiseerd met 97% berberine, het hoogste gehalte dat er op de supplementenmarkt verkrijgbaar is. Het bevat niets anders dan natuurlijke acaciavezels en rijstmeel, oftewel volkomen veilige natuurlijke vulstoffen. Het is echt een technisch hoogstandje, want het is uiterst moeilijk om berberine in een capsule te krijgen.
De therapeutische dosis die gebruikt is in verschillende klinische studies is 200 tot 500 mg, 2 tot 3 maal daags. In dit supplement beiden we supplement in de vorm van een plantaardige capsule van 500 mg die net voor het eten ingenomen dient te worden, eveneens met een frequentie van 2 tot 3 maal daags.
Vindt u het lastig om capsules te slikken? U mag de capsules gerust openen en de inhoud oplossen in een glas water, in een vruchtsapje of in een bakje yoghurt. Berberine wordt namelijk in de mondflora omgezet in dihydroberberine, dat mogelijk zelfs beter geabsorbeerd wordt in de darmen (13).
Update april 2018
Let op: dit product is geen vervanging van een gevarieerd en evenwichtig voedingspatroon en een gezonde levensstijl. U dient zich te houden aan de aanbevelingen voor gebruik, de aanbevolen dagelijkse dosis en de uiterste gebruiksdatum. Niet geschikt voor zwangere en zogende vrouwen en voor kinderen jonger dan 15 jaar. Buiten het bereik van kinderen houden. Droog en koel bewaren.
Reviews
Dit product heeft een beoordeling van 4.7 op 5 sterren.
We hebben 463 beoordelingen verzameld.
77%
17%
3%
1%
2%
30 december 2025
Duidelijke omschrijving van het product en de levering altijd snel
25 juli- 2023
Super werkzaam voor mensen die bepaalde klachten hebben
6 Januari 2021
TRES BIEN,MERCI
9 augustus 2019
S’el geleverd zonder probleem
5 augustus 2019
Voor mij iets te duur in aankoop.Ga ergens zoeken voor goedkopere prijs.
20 april 2019
super product en levering helemaal super snel kunnen andere bedrijven nog een voorbeeld aan nemen
5 juli- 2018
Zeer goed werkend, natuurlijk product. Neem Berberine al jaren en ik heb de indruk dat ik geen diabetische verschijnselen vertoon. Ik ga met het innemen gewoon door en voel mij er goed bij.
9 Januari 2026
très bien pour soutenir la glycémie
29 december 2025
Conforme à les attentes
25 december 2025
J'utilise ce produit depuis de nombreuses annéesTrès efficace pour diabète 2 et cardiologie.
24 december 2025
joyeux noel la reunion
12 december 2025
Habe noch nicht nachgetestet, wie effektiv alles ist. Mein Wohlbefinden seit der Einnahme ist aber gut.
Heb nog niet getest hoe effectief alles is. Mijn welzijn sinds de inname is echter goed.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 december 2025
Cumple con su función
Vervult zijn functie
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 december 2025
Mi dispiace non essermi accorta che non contiene cromo e piperina, ingredienti che l’avrebbero reso più effficace
Het spijt me dat ik niet heb gemerkt dat het geen chroom en piperine bevat, ingrediënten die het effectiever zouden hebben gemaakt.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
22 november 2025
19 november 2025
J utilise ce produit depuis quelques temps, après plusieurs analyses mon cholestérol baisse progressivement
Ik gebruik dit product al een tijdje, na verschillende analyses daalt mijn cholesterol geleidelijk.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
17 november 2025
Das Produkt wirkt sehr gut. Ich werde es weiter empfehlen.
Het product werkt zeer goed. Ik zal het aanbevelen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
17 november 2025
1 prise par jour et un maintien de mon poids, c'rst bien
1 inname per dag en het behouden van mijn gewicht, dat is goed
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
3 november 2025
Produit très efficace
Zeer effectief product
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
25 oktober 2025
23 oktober 2025
Très bon produit.. correspond à mes attentes. L'hémoglobine glyquee est bien stable.
Zeer goed product.. voldoet aan mijn verwachtingen. De geglycosyleerde hemoglobine is goed stabiel.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
17 oktober 2025
Bon produit qui permet de stabiliser le diabète de type II. J'en recommande régulièrement.
Goed product dat helpt bij het stabiliseren van type II diabetes.
Ik beveel het regelmatig aan.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 oktober 2025
Llevo años consumiendo y hasta hoy perfecto
Ik gebruik het al jaren en tot nu toe perfect.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 oktober 2025
La présentation en gélules ne me sied pas , j’ai beaucoup de mal à digérer et il n’est pas fait mention de la possibilité d’ouvrir les gélules et comment prendre le produit.
De presentatie in capsules bevalt me niet, ik heb veel moeite met verteren en er wordt niet vermeld of het mogelijk is de capsules te openen en hoe het product in te nemen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
8 oktober 2025
8 oktober 2025
Pas assez de recul pour constater un résultat..
Niet genoeg afstand om een resultaat te zien.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
2 oktober 2025
27 september 2025
Cela fait même pas un mois que je prends de la verve rien. Beaucoup trop trop pour avoir des effets !
Het is nog geen maand dat ik verveine neem. Veel te veel om effecten te hebben!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
25 september 2025
A régler mes problèmes de diarrhée lié à mon traitement pour le diabète et m'a permis de diminuer le dosage de moitié mon traitement.
Mijn problemen met diarree als gevolg van mijn behandeling voor diabetes oplossen en het heeft me in staat gesteld om de dosering van mijn behandeling te halveren.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
31 juli- 2025
Buon prodotto anzi di qualita'. Grazie
Ordinero' al piu' presto. Grazie
25 juli- 2025
Très bon produit, fait baisser la glycémie.
Zeer goed product, verlaagt de bloedsuikerspiegel.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 juni- 2025
Produit correspondant entièrement à mes attentes et que je trouve complètement adapté.
Product dat volledig aan mijn verwachtingen voldoet en dat ik volledig geschikt vind.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 juni- 2025
Réponds parfaitement
Reageert perfect
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
2 juni- 2025
12 mei 2025
j'utilise ce produit depuis de nombreuse années sa aide modérément a voir par la suite
ik gebruik dit product al vele jaren, het helpt matig, we zullen zien hoe het verder gaat
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 april 2025
Produit me donnant toute satisfaction
Product dat me volledig tevreden stelt
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 april 2025
Produit efficace qui me permet de maintenir ma glycémie dans la norme acceptable.
5 april 2025
depuis 2 mois je prends la berberine , j'ai diminué mon taux de glycémie , gélules facile à prendre et produit efficace sans effet secondaire
sinds 2 maanden neem ik berberine, ik heb mijn bloedsuikerspiegel verlaagd, capsules zijn gemakkelijk in te nemen en het product is effectief zonder bijwerkingen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 april 2025
25 februari 2025
Ce produit a totalement éliminé mon diabète en 6 mois...
Dit product heeft mijn diabetes in 6 maanden volledig geëlimineerd.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
17 februari 2025
Bonjour je me fournis en Berberine chez vous depuis quelques années avant de recommander j'ai lu que la meilleure se trouvait chez TerraVita qu'en pensez-vous ?
Hallo
ik koop al een paar jaar Berberine bij jullie
voordat ik opnieuw bestel, las ik dat de beste bij TerraVita te vinden is
wat denken jullie daarvan?
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
13 februari 2025
j'arrive avec 2 gélules par jour à contenir mon diabète
ik slaag erin met 2 capsules per dag mijn diabetes onder controle te houden
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 Januari 2025
Funziona esattamente come mi avevano detto perciò lo consiglierei a chiunque.
Het werkt precies zoals ze me hadden verteld, dus ik zou het aan iedereen aanraden.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 Januari 2025
Me Conviens très bien
Ik
Past heel goed
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
8 Januari 2025
Spitzenqualität. Höhere Dosierung für effektive Wirkung notwendig. Absolut wichtiger Wirkstoff für grundlegende Supplementierung.
Topkwaliteit. Hogere dosering nodig voor effectieve werking. Absoluut belangrijk ingrediënt voor fundamentele supplementatie.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
8 december 2024
26 november 2024
La facture de FedEx pour mon dernier envoi, est plus cher que le Produit. aussi je ne cde plus de marchandises à votre Maison. Salutations. F-Dumont
De factuur van FedEx voor mijn laatste zending is duurder dan het product. Daarom bestel ik geen goederen meer bij uw bedrijf. Groeten, F-Dumont.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 november 2024
Je prende régulièrement de la berbérine et elle est très efficace sur les intestins particulièrement
Ik neem regelmatig berberine en het is zeer effectief voor de darmen, vooral.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 november 2024
Je n'ai pas assez de recul
Ik heb niet genoeg afstand.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
29 oktober 2024
Es scheint zu wirken. Da ich aber noch ein weiteres Nahrungsergänzungsmittel nehme, kann ich die Einzelwirkung von Berberine noch nicht so richtig beurteilen. Das werde ich erst, wenn das ältere Mittel aufgebraucht ist und ich nur noch auf Berberine setze.
Het lijkt te werken. Maar omdat ik nog een ander voedingssupplement neem, kan ik het individuele effect van berberine nog niet echt beoordelen. Dat zal ik pas kunnen doen als het oudere middel op is en ik alleen nog op berberine vertrouw.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
24 oktober 2024
Lo consumo habitualmente
Ik gebruik het regelmatig.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 september 2024
J'utilise ce produit pour traiter le diabète etles problèmes cardiaques.Très efficace.
Ik gebruik dit product om diabetes en hartproblemen te behandelen. Zeer effectief.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
3 september 2024
Estoy muy contenta con el uso de BERBERINE, me mantiene bien controlada mi Diabetes tipo II. Pero además de toda la descripcion e informacion que ofrecen sobre el producto, me gustaria que informaran sobre la posible interaccion que pudiera presentar con los medicamentos de la medicina convencional por otras patologias, por la duracion de la toma, que ocurre si se interrumpe... No me gusta que hayan cambiando el diseño de los envases, y, la letra que los acompaña sigue siendo muy pequeña, casi no la puedo leer. Me gustaria si es posible que viniese tambien en español. En cuanto al precio, si el tratamiento es de larga duracion, es caro. Todo depende de cuanto tiempo haya que estar tomandolo. Me gustaria volver a recibir de SuperSmart inforamacion, como la que me enviaban antes de la pandemia, pues a veces tengo mucha dificultad para encontrar la forma de conectar para poder hacer pedidos. GRACIAS
1 september 2024
Lo toma un familiar por que la tiroides no le funciona y le descontrola la glucosa. Por ahora se le mantiene justo en el límite o un poquito por encima.
Een familielid neemt het omdat zijn schildklier niet goed werkt en zijn glucose ontregelt. Voor nu blijft het precies op de grens of een beetje erboven.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
31 augustus 2024
Je commence tout juste je verrai à ma prochaine prise de sang si mon cholestérol a baissé
Ik ben net begonnen, ik zal bij mijn volgende bloedonderzoek zien of mijn cholesterol is gedaald.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 augustus 2024
Très efficace sur diabète Je recommande
Zeer effectief bij diabetes. Ik beveel het aan.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
21 augustus 2024
Ce produit correspond parfaitement à mes attentes
Dit product voldoet perfect aan mijn verwachtingen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 augustus 2024
Les kilos s’envolent !
De kilo's vliegen eraf!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 augustus 2024
Mi consente di tenere sotto controllo la glicemia
Het stelt me in staat mijn bloedsuikerspiegel onder controle te houden.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 augustus 2024
31 juli- 2024
Produit conforme livré rapidement
Product conform geleverd snel
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
28 juli- 2024
Fantastique effet symbiotique ! Fantastuque sur l'effet sassiete. Confort intestinal maximum. Meilleure vue, meilleur sommeil et gestion du stress. J'aurais dû prendre + grand soin de mon "2ème cerveau" dès la sirtie de ce complément ! Bien que j'aie une alimentation équilibrée depuis + de 20 ans et que je ne souffre pas du syndrome métabolique. En tant que praticienne de santés je le recommande chaleureusement. Je confirme qu'il faut avoir l'estomac vide pour avoir tous les effets de la Berberine, on peut cependant avoir pris sa ration de fruit d'avant repas (les fruits ne stimulant ps la sécrétion de suc gastrique, l'estomac devient vide dès après passage du fruit, si consommé nature).
Fantastisch symbiotisch effect! Fantastisch voor het verzadigingsgevoel. Maximale darmcomfort. Beter zicht, betere slaap en stressbeheer. Ik had beter voor mijn "2e brein" moeten zorgen sinds de introductie van dit supplement! Hoewel ik al meer dan 20 jaar een uitgebalanceerd dieet heb en niet lijd aan het metabool syndroom. Als gezondheidsbeoefenaar beveel ik het van harte aan. Ik bevestig dat je een lege maag moet hebben om alle effecten van Berberine te ervaren, maar je kunt wel je portie fruit voor de maaltijd hebben genomen (fruit stimuleert de afscheiding van maagsap niet, de maag wordt leeg zodra het fruit is gepasseerd, als het puur wordt geconsumeerd).
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
20 juli- 2024
L’utilise depuis un mois, verrez en septembre si les résultats escomptés sont là
Gebruik het sinds een maand, zal in september zien of de verwachte resultaten er zijn.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
10 juli- 2024
Pour baisser glycémie. Diabète type2
Om de bloedsuikerspiegel te verlagen. Type 2 diabetes
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
28 juni- 2024
Bon produit efficace
Goed en effectief product
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
26 juni- 2024
En 3 mois je n ai pas repris de poids et ça m'a fait baissé ma glycémie
In 3 maanden ben ik niet aangekomen en het heeft mijn bloedsuikerspiegel verlaagd
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
20 juni- 2024
Très bon produit que j’utilise régulièrement.
Zeer goed product dat ik regelmatig gebruik.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 juni- 2024
9 juni- 2024
Produit pris depuis des années et efficace
Product al jaren gebruikt en effectief
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 juni- 2024
Très efficace pour reguler la glycémie, j'en suis très contente
Zeer effectief voor het reguleren van de bloedsuikerspiegel, ik ben er erg tevreden mee
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 juni- 2024
El producto OPTIVISION, aun no puedo valorarlo, porque acabo de empezar a usarlo. Me parece un poco caro. Creo que hay productos que si su composicion lo permite deberian servir para varias molestias a tratar. Yo, queria haber comprado algo para la audicion, pero ya me suponia mucho gasto en dinero.
Het product OPTIVISION kan ik nog niet beoordelen, omdat ik het net ben begonnen te gebruiken. Het lijkt me een beetje duur. Ik denk dat er producten zijn die, als hun samenstelling het toelaat, voor verschillende klachten zouden moeten dienen. Ik wilde iets kopen voor het gehoor, maar dat zou me al te veel geld kosten.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 juni- 2024
Lo estoy usando desde hace muchos años, y, deberian avisar que no se debe interrumpir, pues su efecto desaparece y revierte la mejoria alcanzada. Durante un tiempo no lo usé porque no tenia acceso a poderlo pedir, crei que no pasaria nada, por el mucho tiempo que lo habia estado usando. Pero he tenido que volver a usarlo porque he retocedido con todo el avance que habia hecho en mi control del azucar. Creo que ponen poca informacion sobre el uso regular, y/o mantenimiento de toma de sus productos. Por lo demás espero volver a alcanzar la mejoria que logré y que hizo estar muy satisfecha de su uso.
Ik gebruik het al vele jaren, en ze zouden moeten waarschuwen dat je het niet moet onderbreken, want het effect verdwijnt en de verbetering die je hebt bereikt, keert terug. Een tijdje heb ik het niet gebruikt omdat ik geen toegang had om het te bestellen, ik dacht dat er niets zou gebeuren omdat ik het al zo lang gebruikte. Maar ik moest het weer gaan gebruiken omdat ik achteruitging met alle vooruitgang die ik had geboekt in mijn suikercontrole. Ik denk dat ze weinig informatie geven over het regelmatig gebruik en/of het onderhoud van hun producten. Verder hoop ik de verbetering die ik had bereikt weer te bereiken en weer zeer tevreden te zijn met het gebruik ervan.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 mei 2024
M’aide beaucoup pour ma glycémie
Helpt me veel met mijn bloedsuikerspiegel
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
27 mei 2024
Ma glycémie a baissée moins de fringale et une perte de poids produit efficace
Mijn bloedsuikerspiegel is gedaald, minder hongergevoel en gewichtsverlies, effectief product
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
26 mei 2024
Très bon produit je pense à évaluer après examen sanguin glycémie et cholestérol.
Zeer goed product, ik denk eraan het te evalueren na een bloedonderzoek naar bloedsuiker en cholesterol.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 mei 2024
Aide efficace contre l'excès de sucre.
Effectieve hulp tegen overtollige suiker.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
14 mei 2024
precieux et pas que pour la glycemie
waardevol en niet alleen voor de bloedsuikerspiegel
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 mei 2024
Très efficace sur la perte de poids
Zeer effectief bij gewichtsverlies
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 mei 2024
Ce n'est pas la première fois que j'utilise la Berbérine et j'en suis vraiment satisfaite.
Dit is niet de eerste keer dat ik Berberine gebruik en ik ben er echt tevreden over.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 mei 2024
produit indispensable à mon sens
onmisbaar product naar mijn mening
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
25 april 2024
Bon produit m à fait perdre 1 kilos j attends mon 2eme produit poir voire une différence sur ma.glycemie
Goed product, ik ben 1 kilo afgevallen. Ik wacht op mijn 2e product om een verschil in mijn bloedsuikerspiegel te zien.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 april 2024
Ma glycémie va mieux. Merci la berberîe.
Mijn bloedsuikerspiegel is beter. Dank je wel, berberine.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 april 2024
Excellent. Fait ce que je veux.
Uitstekend. Doet wat ik wil.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
12 april 2024
bonjour ca fait des année que j utilise la berberine en complement pour mes traitement et je nais pas me plaindre ce produit corespond a mes attentes je le recommande viveman au nouvel utilisateur salutations la REUNION
Hallo, ik gebruik al jaren berberine als aanvulling op mijn behandelingen en ik heb niets te klagen. Dit product voldoet aan mijn verwachtingen en ik raad het ten zeerste aan aan nieuwe gebruikers. Groeten, La Réunion.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 april 2024
bien domage un peu cher
jammer, een beetje duur
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 april 2024
Remplace avantageusement un médicament.
Vervangt op voordelige wijze een medicijn.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 april 2024
Génial diabéte jugulé
Geweldig, diabetes onder controle.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
3 april 2024
Il est évident que la prise de Berberine contribue à faire baisser mon taux de glycémie.
Het is duidelijk dat het innemen van Berberine helpt mijn bloedsuikerspiegel te verlagen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
21 maart 2024
client depuis plusieurs années, toujours contant des produits et du service Merc
klant sinds vele jaren, altijd tevreden over de producten en de service. Bedankt
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 maart 2024
Mon époux utilise BERBERINE depuis plusieurs années et nous vous avons donné notre avis (très bon) plusieurs fois. MERCI de ne plus nous poser cette question. MERCI également de votre produit excellent
Mijn echtgenoot gebruikt BERBERINE al meerdere jaren en we hebben u meerdere keren onze mening (zeer goed) gegeven. BEDANKT dat u ons deze vraag niet meer stelt. BEDANKT ook voor uw uitstekende product.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
28 februari 2024
Diabète de type 2 diminution du dosage de médicament grâce à l'apport en berbérine
Type 2 diabetes vermindering van de medicatiedosering dankzij de inname van berberine
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
27 februari 2024
Conforme à mes attentes
Voldoet aan mijn verwachtingen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
21 februari 2024
Problèmes cardiaques,en partie, stabilisés.
Hartproblemen, deels gestabiliseerd.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 februari 2024
Je connaissais déjà la Berbérine. Je connais son efficacité.
Ik kende Berberine al. Ik ken de effectiviteit ervan.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 februari 2024
Bon début de traitement
Goede start van de behandeling
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 februari 2024
9 februari 2024
rien de plus que, pour tous les types 2 à essayer.
niets meer dan, voor alle types 2 om te proberen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
7 februari 2024
Produit répondant à mes attentes
Product voldoet aan mijn verwachtingen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 februari 2024
très bien pour gestion diabète type 2
erg goed voor het beheer van type 2 diabetes
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
2 februari 2024
Excellent produit
Uitstekend product
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
2 februari 2024
Toujours très satisfaite de l'efficacité des produits SuperSMart. Le dosage de leur berbérine permet de bien contrôler sa glycémie. A aussi un effet sur le cholestérol
Altijd zeer tevreden over de effectiviteit van de producten van SuperSmart. De dosering van hun berberine helpt om de bloedsuikerspiegel goed te controleren. Heeft ook een effect op het cholesterol.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
31 Januari 2024
De qualité et très utile .
Van goede kwaliteit en zeer nuttig.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
28 Januari 2024
Produit de bonne qualité, J'attende les résultats de test sanguins.
Product van goede kwaliteit, ik wacht op de resultaten van bloedtesten.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
25 Januari 2024
Ce produit a été vraiment exceptionnel dès le 5e jour. Toutes les douleurs ont disparu. Impressionnant pour le problème que j'avais.
Dit product was echt uitzonderlijk vanaf de 5e dag. Alle pijnen zijn verdwenen. Indrukwekkend voor het probleem dat ik had.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
24 Januari 2024
EXCELENTE PRODUCTO EN CALIDAD/PRECIO
UITSTEKEND PRODUCT IN KWALITEIT/PRIJSVERHOUDING
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 Januari 2024
Parfait et efficace
Perfect en effectief
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
20 Januari 2024
Produit connu et utilisé de longue date et me convient parfaitement.
Bekend en lang gebruikt product dat perfect bij mij past.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 Januari 2024
18 Januari 2024
Remplace avantageusement les produits chimiques pour les mêmes affections
Vervangt op voordelige wijze de chemische producten voor dezelfde aandoeningen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 Januari 2024
8 Januari 2024
He empezado hace poco a tomarlo y todavía no he comprobado sus efectos totalmente
Ik ben er pas net mee begonnen en heb de effecten nog niet volledig kunnen beoordelen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 Januari 2024
Permet de stabiliser le taux de glycémie efficacement
Stabiliseert effectief de bloedsuikerspiegel.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 Januari 2024
Bon pour les troubles gastro-intestinaux et excellent anti cholestérol.
Goed voor gastro-intestinale problemen en uitstekend tegen cholesterol.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
2 Januari 2024
le meilleur produit pour le diabète de type II
het beste product voor type II diabetes
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
28 december 2023
Je pense que c'est un bon produit Mais il n'est pas assez fort pour moi
Ik denk dat het een goed product is, maar het is niet sterk genoeg voor mij.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
27 december 2023
Très satisfait de ce produit que je prends depuis longtemps.
Zeer tevreden over dit product dat ik al lange tijd gebruik.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 december 2023
Complément très satisfaisant
Zeer bevredigend supplement
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
21 december 2023
Au bout de 15 jours effets positifs diminution du diabète.
Na 15 dagen positieve effecten, vermindering van diabetes.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
21 december 2023
Très bon résultat
Zeer goed resultaat
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
21 december 2023
21 december 2023
Bon produit. Associé à une alimentation kéto, la glycémie baisse de façon notoire,
Goed product. In combinatie met een keto-dieet daalt de bloedsuikerspiegel aanzienlijk.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
20 december 2023
Super buen producto me está salvando de tomar metformina (que me sienta muy mal) y me hace el mismo efecto sin contraindicaciiones ni efectos secundarios
Super goed product, het bespaart me van het nemen van metformine (waar ik me erg slecht door voel) en het heeft hetzelfde effect zonder contra-indicaties of bijwerkingen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 december 2023
calidad/precio excelente
kwaliteit/prijs uitstekend
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 december 2023
complément intéressant pour contrôler la glycémie et apporter des bienfaits à la sphère gastro-intestinale
interessant supplement om de bloedsuikerspiegel te beheersen en voordelen te bieden voor de gastro-intestinale sfeer
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 december 2023
Les deux produits sont efficaces et répondent à mon attentent et celle du médecin.
Beide producten zijn effectief en voldoen aan mijn verwachtingen en die van de arts.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
14 december 2023
Produits chers mais ils sont efficaces et avec la réduction c'est encore possible de les acheter .De plus pas d'effets secondaires , cela est important
Dure producten, maar ze zijn effectief en met de korting is het nog mogelijk om ze te kopen. Bovendien geen bijwerkingen, dat is belangrijk.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
12 december 2023
Parfait pour baisser la glycémie. Diabète type 2.
Perfect om de bloedsuikerspiegel te verlagen. Type 2 diabetes.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
7 december 2023
BERBERINE pris en prévention, juste avant les consommations fortes et inhabituelles de sucre, afin de réduire la glycémie
Berberine ingenomen ter preventie, net voor de sterke en ongebruikelijke consumptie van suiker, om de bloedsuikerspiegel te verlagen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 december 2023
un traitement parfait
een perfecte behandeling
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
2 december 2023
client de longue date, toujours satisfait des produit et dduservice FD
langdurige klant, altijd tevreden over de producten en de service FD
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 december 2023
Produit conforme à mes attentes Livraison rapide
Product voldoet aan mijn verwachtingen Snelle levering
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 december 2023
molécule à découvrir absolument ! dosage parfait 2 gél. 3 x /jr pendant 5 jrs
molecuul die je absoluut moet ontdekken! perfecte dosering 2 caps. 3 x /dag gedurende 5 dagen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
26 november 2023
très bon produit mon mari l'utilise depuis plusieurs années, plus de diabète de type II
Zeer goed product, mijn man gebruikt het al jaren, geen type II diabetes meer.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
20 november 2023
Ayuda a controlar el azúcar en sangre, pero a largo plazo.
Helpt de bloedsuikerspiegel onder controle te houden, maar op de lange termijn.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 november 2023
Bien sûr, assez coûteux, mais efficace ,
Natuurlijk, vrij prijzig, maar effectief,
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
15 november 2023
13 november 2023
mon taux de glycémie s'est maintenu.
mijn bloedsuikerspiegel is stabiel gebleven.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 november 2023
3 november 2023
bon produit à voir dans le temps
goed product, afwachten hoe het op de lange termijn werkt
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 november 2023
C'est un produit que je suis depuis des années et je suis toujours aussi satisfait quand à so efficacité.
Dit is een product dat ik al jaren gebruik en ik ben nog steeds even tevreden over de effectiviteit ervan.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 oktober 2023
Es un buen producto, y sirve para lo que lo prescriben. Me gustaría fuera un poco más asequible.
Het is een goed product en het dient waarvoor het wordt voorgeschreven. Ik zou willen dat het iets betaalbaarder was.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
28 oktober 2023
produit un peu cher pour moi mais qui fonctionne
product een beetje duur voor mij maar het werkt
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
26 oktober 2023
attendre au moins un mois pour avoir un avis
wacht minstens een maand om een mening te hebben
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
25 oktober 2023
creo que es un producto ideal para mis problemas cardiovasculares.
ik denk dat het een ideaal product is voor mijn cardiovasculaire problemen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 oktober 2023
La berberine, celle proposée, est parfaite pour réparer mes intestins. Selles pour moi redevues normales, avec un protocole différent des recommandations.
De berberine, die hier wordt aangeboden, is perfect om mijn darmen te herstellen. Mijn ontlasting is weer normaal geworden, met een ander protocol dan de aanbevelingen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
12 oktober 2023
27 september 2023
Très bon produit pour le diabète !
Zeer goed product voor diabetes!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
24 september 2023
Un produit qui m'accompagne dans le suivi de mon diabete..
Een product dat mij helpt bij het beheer van mijn diabetes.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 september 2023
You be so good supersmart. You got the vits that we need. :)
Je bent zo goed, Supersmart. Jullie hebben de vitamines die we nodig hebben. :)
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 september 2023
Ce qui serait bien c’est d’avoir un retour «�médical�» à savoir si le produit est toujours efficace car j’ai constaté après des années de prise que les résultats de glycémie sont en augmentation.
Wat goed zou zijn, is om een "medisch" antwoord te krijgen om te weten of het product nog steeds effectief is, omdat ik na jaren van inname heb gemerkt dat de bloedsuikerwaarden toenemen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
7 september 2023
Creo que es bueno
Ik denk dat het goed is
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 september 2023
Très bon produit que j'utilise depuis des années A l'origine a été conseillé par mon médecin
Zeer goed product dat ik al jaren gebruik. Oorspronkelijk aanbevolen door mijn arts.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 september 2023
Seule pas trop de résultat , mais bien avec de la berberine ont obtient des meuilleurs résultats
Alleen niet te veel resultaat, maar samen met berberine krijg je betere resultaten
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
3 september 2023
Conforme à mes attentes
Voldoet aan mijn verwachtingen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 september 2023
La berbérine, un vrai miracle de la nature, contre l'excès de sucre.
Berberine, een echt wonder van de natuur, tegen overtollige suiker.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
29 augustus 2023
22 augustus 2023
Je ne suis pas totalement satisfait, je croyais pouvoir avoir de mieux résultats.
Ik ben niet helemaal tevreden, ik dacht dat ik betere resultaten zou kunnen behalen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
13 augustus 2023
parfait comme d'hab.régule laglycémie, fait perdre du poids
perfect zoals altijd. reguleert de bloedsuikerspiegel, helpt bij gewichtsverlies
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
7 augustus 2023
Très bon produit.
Zeer goed product.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
26 juli- 2023
Bon produit mais semble moins efficace depuis la présentation en gélules.je l'utilise depuis longtemps
Goed product, maar lijkt minder effectief sinds de presentatie in capsules. Ik gebruik het al lang.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
26 juli- 2023
Excellent produit avec effets notoires
Uitstekend product met merkbare effecten
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
22 juli- 2023
Ce produit me donne entière satisfaction
Dit product geeft me volledige tevredenheid
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 juni- 2023
Un produit qui me va bien..
Een product dat goed bij mij past.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 juni- 2023
Je suis toujours très dubitative quant à l'efficacité de ce produit, mais peut-être cela aide-t-il selon le cas. Moi pas, en tous cas.
Ik ben nog steeds erg sceptisch over de effectiviteit van dit product, maar misschien helpt het afhankelijk van het geval. Voor mij niet, in ieder geval.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 juni- 2023
Très efficace pour faire baisser le taux de diabète, on recommande
Zeer effectief om de bloedsuikerspiegel te verlagen, aanbevolen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
10 juni- 2023
Le produit naturel le plus efficace, sur moi, contre les coups de fatigue (hausses de glycémie puis chutes de glycémie) après les repas (ça ne marche peut-être pas chez tout le monde). Je dois cependant prendre double dose pour sentir une réelle différence, 30-40 min avant le début du repas environ.
Het meest effectieve natuurlijke product, voor mij, tegen vermoeidheidsklachten (stijgingen van de bloedsuikerspiegel gevolgd door dalingen van de bloedsuikerspiegel) na de maaltijden (het werkt misschien niet voor iedereen). Ik moet echter een dubbele dosis nemen om een echt verschil te voelen, ongeveer 30-40 minuten voor het begin van de maaltijd.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 juni- 2023
FANTÁSTICO PARA BAJAR EL NIVEL DE AZÚCAR. HE PROBADO OTRAS MARCAS Y NO SON TAN EFECTIVAS
FANTASTISCH OM HET SUIKERNIVEAU TE VERLAGEN. IK HEB ANDERE MERKEN GEPROBEERD EN DEZE ZIJN NIET ZO EFFECTIEF.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 juni- 2023
Produit efficace répondant bien à mes attentes.
Effectief product dat goed aan mijn verwachtingen voldoet.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 juni- 2023
Idem qu'avec le Glucofit
Hetzelfde als met de Glucofit
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
31 mei 2023
Excellent complément ! Depuis que j'en prends, mon hémoglobine glyquée (évaluée par prises de sang régulières) a diminué régulièrement au point d'atteindre des chiffres normaux.
Uitstekend supplement! Sinds ik het gebruik, is mijn geglyceerde hemoglobine (gemeten door regelmatige bloedafnames) gestaag gedaald tot normale waarden.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
31 mei 2023
30 mei 2023
tres bon produit, fait le job.Remplace bien la metformine,pour faire baisser la glycemie, mais provoque au debut un peu de constipation.
Zeer goed product, doet zijn werk. Vervangt metformine goed om de bloedsuikerspiegel te verlagen, maar veroorzaakt in het begin een beetje constipatie.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
29 mei 2023
Efficace et me protège de certains problèmes
Effectief en beschermt me tegen bepaalde problemen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
22 mei 2023
Merci mais depuis le réapprovisionnement la qualiest bizarre car ont restant des vaumissemt 15 minutes après absorption bref c'est quand même exceptionnel pour les gens qui ont du diabète merci
Bedankt, maar sinds de herbevoorrading is de kwaliteit vreemd, want we ervaren misselijkheid 15 minuten na inname. Kortom, het is toch uitzonderlijk voor mensen met diabetes, bedankt.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
15 mei 2023
deja repondu, rien à dire de plus, quand c'est bon, c'est bon.
al beantwoord, niets meer te zeggen, als het goed is, is het goed.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
15 mei 2023
ES UN PRODUCTO QUE A MI, ME SIENTA PERFECTAMENTE.
HET IS EEN PRODUCT DAT VOOR MIJ PERFECT WERKT.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 mei 2023
Excellent rapport qualité/prix.
Uitstekende prijs-kwaliteitverhouding.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 april 2023
9 april 2023
einwandfrei. hohe dosierung pro kapsel des reinen wirkstoffes
perfect. hoge dosering per capsule van de pure werkzame stof
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 april 2023
Bien, satisface mis espectativas
Goed, het voldoet aan mijn verwachtingen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 april 2023
Avis favorable sur les bienfaits du produit
Positieve beoordeling over de voordelen van het product
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 april 2023
Réduit un peu la glycémie
Vermindert de bloedsuikerspiegel een beetje
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 april 2023
Utlisé pour remplacer METFORMINE
Gebruikt ter vervanging van METFORMINE
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
3 april 2023
a ma connaisance le meilleur regulateur du taux de glycemie disponible
Naar mijn weten de beste regulator van de bloedsuikerspiegel die beschikbaar is
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
31 maart 2023
J’ai de très bons résultats avec ce produits
Ik heb zeer goede resultaten met dit product.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 maart 2023
Ce produit que je prends depuis 2017 a permis de stabiliser mon diabète sans avoir à prendre de la metformine. Il faut quand faire attention à ce qu'on mange et ne pas faire d'excès de sucre. Mon endocrino, qui ne connaissait pas la berberine en 2017, au vu de mes résultats d'analyse est très content des résultats dans mon cas. Il n'y a pas d'effet secondaire, j'espère pouvoir continuer encore longtemps ce traitement
Dit product, dat ik sinds 2017 gebruik, heeft mijn diabetes gestabiliseerd zonder dat ik metformine hoefde te nemen. Je moet wel opletten wat je eet en geen overmatige hoeveelheden suiker consumeren. Mijn endocrinoloog, die in 2017 nog niet bekend was met berberine, is zeer tevreden met de resultaten in mijn geval, gezien mijn analyse-resultaten. Er zijn geen bijwerkingen, en ik hoop deze behandeling nog lang te kunnen voortzetten.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
28 maart 2023
efficace pour le diabète et sans effet secondaire , c'est le top
effectief voor diabetes en zonder bijwerkingen, het is top
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
25 maart 2023
I use Berberine since approximately 10 years now to control the level of sugar in my blood and it works allright...
Ik gebruik Berberine nu al ongeveer 10 jaar om mijn bloedsuikerspiegel onder controle te houden en het werkt prima...
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
25 maart 2023
Magique pour régulation glycémie p
Magisch voor het reguleren van de bloedsuikerspiegel
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
20 maart 2023
Je l'utilise depuis longtemps sans problème.
Ik gebruik het al lange tijd zonder problemen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
20 maart 2023
17 maart 2023
ottimo prodotto funzione per abbassare glicemia
uitstekend product werkt om de bloedsuikerspiegel te verlagen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 maart 2023
avis médical favorable
gunstig medisch advies
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 maart 2023
Sehr gutes Produkt
Zeer goed product
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
3 februari 2023
non sono ancora in grado di esprimere un giudizio sul prodotto, potrò farlo solo dopo un esame
ik ben nog niet in staat om een oordeel over het product te geven, dat kan ik pas na een onderzoek doen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
27 Januari 2023
Buen producto para problemas de azúcar y de colesterol. La relación calidad-precio es inmejorable.
Goed product voor problemen met suiker en cholesterol. De prijs-kwaliteitverhouding is onovertroffen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
27 Januari 2023
Produit très efficace.
Zeer effectief product.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 Januari 2023
He probado berberina de varias marcas y para mí esta en la mejor para la diabetes tipo 2. Las otras marcas no me controlan con la misma eficacia
Ik heb berberine van verschillende merken geprobeerd en voor mij is dit de beste voor type 2 diabetes. De andere merken beheersen het niet met dezelfde effectiviteit.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
17 Januari 2023
13 Januari 2023
Un bon remède naturel et pas trop couteux contre les aléas du déséquilibre glycémique. Remplace efficacement le traitement classique à bas e de M..........
Een goed natuurlijk middel en niet te duur tegen de grillen van een onbalans in de bloedsuikerspiegel. Vervangt effectief de klassieke behandeling op basis van M..........
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 oktober 2022
J'utilise la Berberine depuis plusieurs années, ce qui permet de réguler mon taux de glucides. J'associe une alimentation méditerranéenne.
Ik gebruik al jaren Berberine, wat helpt om mijn koolhydraatgehalte te reguleren. Ik combineer het met een mediterraan dieet.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
27 september 2022
mon diabète a diminué
mijn diabetes is verminderd
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
20 augustus 2022
De même que le précédent qui d'ailleurs en association donnent de très bons résultats.
Net als de vorige, die trouwens in combinatie zeer goede resultaten opleveren.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 augustus 2022
Good product that works well, but a bit expensive.
Goed product dat goed werkt, maar een beetje duur.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
26 juni- 2022
Très efficace et bien dosé.
Zeer effectief en goed gedoseerd.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 mei 2022
J'en prends depuis des annees et suis tres satisfaite
Ik neem het al jaren en ben zeer tevreden.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 april 2022
super produit qui n'a juste qu'une constipation passagère et qui fait le travail.la metformine débouche sur l'acidiose lactique .le choix est vite fait:Si la
super product dat alleen tijdelijke constipatie veroorzaakt en zijn werk doet. metformine leidt tot melkzuuracidose. de keuze is snel gemaakt: Als de
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 maart 2022
Remplace aisément la METFORMINE sans les effets indésirables.
Vervangt gemakkelijk METFORMINE zonder de bijwerkingen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 februari 2022
5 februari 2022
7 Januari 2022
Un des rares produit dont on peut évaluer l'efficacité par une prise de sang. C'est un des très peu nombreux anti-diabète à avoir une petite efficacité. Pas un produit miracle, mais il n'en existe malheureusement pas.
Een van de weinige producten waarvan de effectiviteit kan worden beoordeeld door een bloedtest. Het is een van de zeer weinige anti-diabetes producten met een kleine effectiviteit. Geen wondermiddel, maar helaas bestaat dat niet.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 Januari 2022
Perfekt um Diabetes zu vermeiden
Perfect om diabetes te voorkomen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 december 2021
La berbérine me permet de réguler un diabète sans avoir d'effets secondaires contrairement aux médicaments . Supersmart est un site à recommander
Berberine stelt me in staat om diabetes te reguleren zonder bijwerkingen, in tegenstelling tot medicijnen. Supersmart is een site die ik kan aanbevelen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
12 december 2021
La qualité est au rendez-vous (pas de poudre en liberté dans le flacon. Il semble qu’il y ait une action sur la glycémie.
De kwaliteit is aanwezig (geen poeder los in de fles). Het lijkt erop dat het een effect heeft op de bloedsuikerspiegel.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
7 december 2021
aucune influence sur glycémie, malgré des mois de cure
geen invloed op de bloedsuikerspiegel, ondanks maanden van gebruik
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
21 november 2021
Estoy contenta y satisfecha con ambos preparados. ¿Por cuanto tiempo se deben tomar? ¿Hay que hacer temporadas de descanso?. Tomo Berberine 500mg desde hace ya algunos años pues padezco Diabetes tipo 2 no insulino- dependiente, y, me ayuda mucho a controlar los niveles de glucosa en sangre, cuando a veces me salgo con la alimentacion, pues padezco tambien de sindrome metabolico(hipotiroidismo, colesterol, hipertension), y debo llevar mucho control con la dieta, con los alimentos, lo que a veces es muy monotono y pesado y muy dificil de realizar. ¿No podrian escribir alguna tabla con el indice glucemico por gramos de cada alimento? ¿No pueden fabricar algun preparado que sirva para controlar a varios o todos a la vez los problemas que forman el sindrome metabolico, y, tener que ingerir tantas pastillas en cada toma?. Con Advanced Fat Burner muchas veces consigo controlar las ganas de comer, este preparado me funciona bastante bien. ¿Tienen algun preparado para el higado graso?. Me gustaria poder solucionar la caida del pelo, conseguir bajar de peso, el cansancio. Espero que mi opinion les sirva, y, puedan seguir ayudandome como hasta ahora. Muchas GRACIAS...!
Ik ben tevreden en voldaan met beide preparaten. Hoe lang moeten ze worden ingenomen? Moet je pauzes inlassen? Ik neem al enkele jaren Berberine 500mg omdat ik lijd aan type 2 diabetes die niet insuline-afhankelijk is, en het helpt me veel om mijn bloedsuikerspiegel onder controle te houden, vooral wanneer ik soms afwijk van mijn dieet. Ik heb ook het metabool syndroom (hypothyreoïdie, cholesterol, hypertensie) en moet mijn dieet en voeding goed in de gaten houden, wat soms erg eentonig, zwaar en moeilijk vol te houden is. Kunnen jullie geen tabel maken met de glycemische index per gram van elk voedingsmiddel? Kunnen jullie geen preparaat maken dat helpt om meerdere of alle problemen van het metabool syndroom tegelijk te beheersen, zodat ik niet zoveel pillen per keer hoef in te nemen? Met Advanced Fat Burner kan ik vaak mijn eetlust onder controle houden, dit preparaat werkt vrij goed voor mij. Hebben jullie een preparaat voor leververvetting? Ik zou graag mijn haaruitval willen oplossen, afvallen en mijn vermoeidheid verminderen. Ik hoop dat mijn mening nuttig voor jullie is en dat jullie me kunnen blijven helpen zoals tot nu toe. Heel erg BEDANKT...!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
15 november 2021
Despuès de meses de tratamiento con dos càpsulas diarias, los anàlisis arrojan el nivel de azùcar en sangre totalmente normal
Na maanden van behandeling met twee capsules per dag, laten de analyses zien dat het bloedsuikerniveau volledig normaal is.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 november 2021
Produit qui me donne satisfaction dans la mesure ou j'arrive à stabiliser mes constantes glycémiques
Product dat me voldoening geeft omdat ik erin slaag mijn glycemische waarden te stabiliseren
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
14 oktober 2021
Ce produit m’a été recommandé par mon médecin. Le dosage est élevé en principes actifs. Cela maintient mon diabète 2 sans trop modifier mon alimentation.
Dit product werd mij aanbevolen door mijn arts. De dosering is hoog in actieve bestanddelen. Dit houdt mijn diabetes type 2 onder controle zonder mijn dieet te veel aan te passen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
13 oktober 2021
produit efficace
doeltreffend product
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
20 september 2021
Vielkönner Berberine
Veelkunner Berberine
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
12 september 2021
Merci ! J'ai guéri mon diabète grâce à la berberine ! Mon médecin n'en croyait pas ses yeux ! Le pire, c'est que suite à question : "alors ? Allez-vous conseiller la berbérine à vos patients autre que le produit chimique ?" Réponse.... négative !!! No comment dans ce monde qui tourne à l'envers !!!!
Bedankt! Ik heb mijn diabetes genezen dankzij berberine! Mijn arts kon zijn ogen niet geloven! Het ergste is dat op de vraag: "Dus? Gaat u berberine aanbevelen aan uw patiënten in plaats van het chemische product?" Het antwoord... negatief!!! Geen commentaar in deze wereld die op zijn kop staat!!!!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 september 2021
Produit de très bonne qualité
Product van zeer goede kwaliteit
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
10 september 2021
Very quick service and a quality product that works for me
Zeer snelle service en een kwaliteitsproduct dat voor mij werkt
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
7 september 2021
Produto eficaz no que corresponde a descrição do produto, porque as analises clinicas ao sangue assim mostram. Excelente qualidade/preço. Recomendo.
Effectief product dat overeenkomt met de productbeschrijving, omdat klinische bloedonderzoeken dit aantonen. Uitstekende kwaliteit/prijsverhouding. Aanbevolen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
13 augustus 2021
Correspond à mon attente
Voldoet aan mijn verwachting
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
10 augustus 2021
Excellent produit avec un dosage important. Conseillé par ma nutritionniste pour maintenir le niveau de cholestérol stable. C'est l equivalent de la metformine mais 1000 fois meilleur car celui-là provient d une plante naturel utilisé dans la médecine ayurvedique. Je le conseille vivement. Merci Supersmart.
Uitstekend product met een hoge dosering. Aanbevolen door mijn voedingsdeskundige om het cholesterolniveau stabiel te houden. Het is het equivalent van metformine, maar 1000 keer beter omdat dit afkomstig is van een natuurlijke plant die in de ayurvedische geneeskunde wordt gebruikt. Ik raad het ten zeerste aan. Bedankt Supersmart.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 augustus 2021
RAS de négatif je l'utilise désormais depuis plusieurs années Henri KÉPÉNÉKIAN
Niets negatiefs te melden, ik gebruik het nu al meerdere jaren Henri KÉPÉNÉKIAN
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
29 juli- 2021
Depuis des années maintenant je soigne mon diabète(entre autre) avec ce produit (que je recommande)et j'en suis pleinement satisfaite. Le produit est des plus performant et les opérations de commande et d'envoi faciles et rapides. Tous mes remerciements Maryse
Al jaren behandel ik mijn diabetes (onder andere) met dit product (dat ik aanbeveel) en ik ben er volledig tevreden mee. Het product is zeer effectief en de bestel- en verzendprocedures zijn eenvoudig en snel. Mijn dank, Maryse
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 juli- 2021
tout semble normal
alles lijkt normaal
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 juni- 2021
Bon produit efficace et sans effets secondaires peut-être un peu cher
Goed product, effectief en zonder bijwerkingen, misschien een beetje duur.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 juni- 2021
Su consumo me está resultando positivo
Het gebruik ervan bevalt me goed
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
28 mei 2021
MUY BUENA CALIDAD. HE COMPRADO DE OTRAS MARCAS Y NO ME CONTROLA EL AZÚCAR COMO LA BERBERINA DE SUPERSMART
ZEER GOEDE KWALITEIT. IK HEB VAN ANDERE MERKEN GEKOCHT EN ZE CONTROLEREN MIJNS INZIENS DE SUIKER NIET ZOALS DE BERBERINE VAN SUPERSMART
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
22 mei 2021
Resultado correcto
Correct resultaat
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
12 mei 2021
M’aide à contrôler ma glycémie
Helpt me mijn bloedsuikerspiegel te controleren
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
7 mei 2021
Au moins aussi efficace que la Metformine
Minstens zo effectief als Metformine
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 mei 2021
Je n'en vois pas les effets sur la baisse de diabète!
Ik zie geen effect op de verlaging van mijn diabetes!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
10 april 2021
Parfait pour moi. Mon cholestérol a baissé. Je n’ai plus que du Bon et le ratio est parfait grâce à la Berberine.
Perfect voor mij. Mijn cholesterol is gedaald. Ik heb alleen nog maar goede cholesterol en de verhouding is perfect dankzij de Berberine.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
26 maart 2021
26 maart 2021
19 maart 2021
11 maart 2021
C'est un produit pure qui n'as pas d'effets secondaire comme ceux qu'on achète en pharmacie!
Het is een puur product dat geen bijwerkingen heeft zoals die je bij de apotheek koopt!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
10 maart 2021
difficile d'évaluer l'efficacité mais semble avoir un effet car chaque fois que j'ai arrêté d'en prendre ma glycémie était plus difficile à contrôler !!!! alors je continue 1 gélule le matin et une le soir . Reste un peu cher malgré les ristournes de fidélité , aimerai avoir plus de visibilité technique sur l'efficacité car explications un peu flou .
moeilijk om de effectiviteit te beoordelen, maar het lijkt een effect te hebben, want elke keer dat ik stopte met het innemen ervan, was mijn bloedsuikerspiegel moeilijker te controleren !!!! dus ik blijf doorgaan met 1 capsule 's ochtends en een 's avonds. Blijft een beetje duur ondanks de loyaliteitskortingen, zou graag meer technische zichtbaarheid willen hebben over de effectiviteit omdat de uitleg een beetje vaag is.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 maart 2021
8 februari 2021
Lo prendo da anni e mi aiuta col diabete.
Ik gebruik het al jaren en het helpt me met diabetes.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
3 februari 2021
Excellent pour diminuer la glycémie et bon complément aux prèscriptions médicales
Uitstekend om de bloedsuikerspiegel te verlagen en een goede aanvulling op medische voorschriften
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
22 Januari 2021
Bon pour le diabète !
Goed voor diabetes!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 Januari 2021
Remplace la metformine sans les effets secondaires
Vervangt metformine zonder de bijwerkingen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 Januari 2021
Correspond à mes attentes concernant la qualité et l'efficacité de ce produit qui m'a été recommandé par un professionnel. Je recommande
Komt overeen met mijn verwachtingen wat betreft de kwaliteit en de effectiviteit van dit product dat mij werd aanbevolen door een professional. Ik beveel het aan.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 Januari 2021
31 december 2020
Ce produit correspond totalement a mon attente..
Dit product voldoet volledig aan mijn verwachtingen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 december 2020
Sauf que le package est rouge est 1000 au lieu de 500 ça porte à confusion on ne sait pas vraiment pour posologie
Behalve dat het pakket rood is en 1000 in plaats van 500, wat verwarrend is, weet men niet echt wat de dosering is.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
24 november 2020
Je ne ressens pas l’effet immédiat, mais je continue en pensant qu’il a un effet bénéfique à la longue.
Ik voel niet meteen het effect, maar ik ga door in de veronderstelling dat het op de lange termijn een gunstig effect heeft.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 november 2020
Un producto muy bueno para ayudar a bajar los niveles de glucosa. He podido reducir el uso de metformina.
Een zeer goed product om te helpen de glucosespiegels te verlagen. Ik heb het gebruik van metformine kunnen verminderen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 november 2020
Efficacité confirmée par des analyses de sucre dans le sang
Effectiviteit bevestigd door bloedsuikeranalyses
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 november 2020
6 november 2020
M'aide à lutter efficacement contre le diabète depuis plusieurs années associé à un régime alimentaire assez strict sans sucres rapides. Pas de traitement médicamenteux jusqu'à ce jour.
Helpt me al jaren effectief te vechten tegen diabetes in combinatie met een vrij strikt dieet zonder snelle suikers. Tot op heden geen medicamenteuze behandeling.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 oktober 2020
Correspond aux attentes
Voldoet aan de verwachtingen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 oktober 2020
Livraison rapide pour un produit super efficace et sans effets secondaires A recommander
Snelle levering voor een super effectief product zonder bijwerkingen. Aanbevolen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 oktober 2020
très efficace pour le glucose
zeer effectief voor glucose
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
14 oktober 2020
Muy efectivo, mis niveles de glucosa se han reducido por debajo de 100.
Zeer effectief, mijn glucosespiegels zijn gedaald tot onder de 100.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
29 september 2020
wer auf seine Gesundheit und seinen Darm achtet, ist mit diesem Proukt bestens bedient.
Wie op zijn gezondheid en zijn darmen let, is met dit product uitstekend bediend.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 september 2020
top impeccable, rien à dire
top onberispelijk, niets op aan te merken
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 augustus 2020
La formulation en comprimé me paraissait plus efficace que les gellules
De tabletformulering leek me effectiever dan de capsules
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
15 augustus 2020
En ce qui me concerne je prends de la berbérine 500mg. pour maintenir mon diabète à un taux normal et avec la berbérine ça me réussit très bien puisque j'arrive à stabiliser mon H.G. à un taux entre 6,5 et 6,8. J'en utilise depuis plusieurs années car je ne supportais pas la metformine et il fallait que je trouve autre chose, dommage que ce ne soit pas remboursé pas la sécu.
Wat mij betreft neem ik 500 mg berberine om mijn diabetes op een normaal niveau te houden en met berberine lukt dat heel goed, aangezien ik mijn H.G. kan stabiliseren op een niveau tussen 6,5 en 6,8. Ik gebruik het al meerdere jaren omdat ik metformine niet kon verdragen en ik iets anders moest vinden, jammer dat het niet wordt vergoed door de zorgverzekering.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
8 augustus 2020
Ce produit me donne entiere satisfaction ...
Dit product geeft me volledige tevredenheid ...
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
31 juli- 2020
J'utilise Berberine (3 par jour) au lieu de Metformine, (3) sans effets indésirables et n' oublies pas de me plier au même régime. Pour moi c' est la solution., même si je prends en charge les frais de ce traitement.
Ik gebruik Berberine (3 per dag) in plaats van Metformine, (3) zonder bijwerkingen en vergeet niet dat ik hetzelfde dieet volg. Voor mij is dit de oplossing, zelfs als ik de kosten van deze behandeling zelf draag.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 juli- 2020
Je suis très déçu de ce produit qui serai censé remplacer avantageusement la Metformine en cas de diabète de type 2 mais qui ne semble avoir aucun effet sur ma glycémie si bien que je continue le médicament. Peut-être une question de dosage?
Ik ben zeer teleurgesteld over dit product dat zogenaamd de Metformine zou vervangen bij type 2 diabetes, maar dat lijkt geen enkel effect te hebben op mijn bloedsuikerspiegel, zodat ik het medicijn blijf gebruiken. Misschien een kwestie van dosering?
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
26 juli- 2020
Excellent substitut à la metformine : 3 gélules pour 2 dragées Simplement pas remboursé donc un peu cher Sinon c'est parfait
Uitstekende vervanging voor metformine: 3 capsules voor 2 dragees. Gewoon niet vergoed, dus een beetje duur. Verder is het perfect.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
20 juli- 2020
Très bon produit de bonne qualité
Zeer goed product van goede kwaliteit
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 juli- 2020
Elle a finalement compris. Merci.
Ze heeft het uiteindelijk begrepen. Dank je.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
17 juli- 2020
J'utilise ce produit Supersmart depuis des années et en suis très satisfait !
Ik gebruik dit product van Supersmart al jaren en ben er zeer tevreden over!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
3 juli- 2020
Une alternative à la metformine ou autre produits pour améliorer le taux de glycémie dans le sang. La berbérine remplace très bien sans les effets secondaires !
Een alternatief voor metformine of andere producten om de bloedsuikerspiegel te verbeteren. Berberine vervangt het uitstekend zonder bijwerkingen!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 juni- 2020
Considero que son muy imporantes para mi salud
Ik vind ze erg belangrijk voor mijn gezondheid
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
29 juni- 2020
29 juni- 2020
C'est un tres bon medicamrnt Je vais en acheter souvent.
Het is een zeer goed medicijn. Ik ga het vaak kopen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
25 juni- 2020
Efficace. Mais revient à cher quand on le prend toitr l'année
Effectief. Maar het wordt duur als je het het hele jaar door neemt
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 juni- 2020
used for its powerful anti-microbial activity to fight intestinal dysbiosis
gebruikt vanwege zijn krachtige antimicrobiële werking om intestinale dysbiose te bestrijden
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 juni- 2020
Produit qui paraît donner des effets satisfaisants sur le taux de glycémie , mais qui malheureusement n'est pas quantifiable . J'ai demandé une étude plus précise sur ces effets et n'est jamais eu de réponse !! Nous sommes obligé de prendre pour argent comptant les indications de SuperSmart . D'autre part , ayant demandé des précisions à des professionnels de santé sur la Berberine , personne ne connaissait ce produit et son activité sur la glycémie . QUI CROIRE ? ma perception personnelle et mon utilisation me laisse penser que ce produit aide à "lisser" les résultats journaliers de taux glycémique . Ce n'est que mon avis ( utilisateur : diabétique de type 2 ) Je trouve le prix élevé " pour un petit retraité "
Product dat lijkt bevredigende effecten te hebben op de bloedsuikerspiegel, maar helaas niet meetbaar is. Ik heb om een nauwkeurigere studie van deze effecten gevraagd en nooit een antwoord gekregen!! We moeten de aanwijzingen van SuperSmart voor waar aannemen. Bovendien, toen ik om verduidelijking vroeg aan gezondheidsprofessionals over Berberine, kende niemand dit product en zijn werking op de bloedsuikerspiegel. WIE MOET JE GELOVEN? Mijn persoonlijke perceptie en gebruik doen me denken dat dit product helpt om de dagelijkse bloedsuikerwaarden te "egaliseren". Dit is slechts mijn mening (gebruiker: type 2 diabeticus). Ik vind de prijs hoog "voor een kleine gepensioneerde".
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
15 juni- 2020
Me semble moins efficace qu'annoncé.
Lijkt minder effectief dan aangekondigd.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 juni- 2020
excellent produit
uitstekend product
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 juni- 2020
Je prends ce produit depuis deux mois en association avec du chrome. Je n'ai absolument aucune amélioration , ma glycémie a même augmentée. Je suis une alimentation très stricte. Le prix est très excessif.
Ik gebruik dit product al twee maanden in combinatie met chroom. Ik merk absoluut geen verbetering, mijn bloedsuikerspiegel is zelfs gestegen. Ik volg een zeer strikt dieet. De prijs is zeer hoog.
Mr BLOIS,
Nous sommes navrés que notre complément Berberine n'ai pas amélioré votre glycémie, malgré les nombreux témoignages positifs reçus de la part des nos utilisateurs.
La Berbérine extraite de l'Epine Vinette contribue a baissé la glycémie, réduire la perméabilité intestinale et ralentir la synthèse endogène du glucose. Son action fait augmenter la sécrétion d'insuline et stimule également la glycolyse.
La dose thérapeutique utilisée dans la plupart des études cliniques est de 200 à 500 mg, 2 à 3 fois par jour. Dans ce supplément, la berbérine est proposée sous forme d’une gélule végétale de 500 mg à prendre juste avant les repas, selon la même périodicité.
Tout comme les médicaments, l'action des compléments nutritionnels varie en fonction de l'organisme de chacun, l'hygiène de vie etc. C'est pourquoi, il faut tout de même consulter un professionnel de santé avant la prise de ces compléments surtout si des traitements médicamenteux sont utilisés en même temps.
Bien à vous,
Gaëlle - Supersmart
Mr BLOIS,
Het spijt ons dat ons supplement Berberine uw bloedsuikerspiegel niet heeft verbeterd, ondanks de vele positieve getuigenissen van onze gebruikers.
De uit de Berberis gewonnen Berberine helpt de bloedsuikerspiegel te verlagen, de darmpermeabiliteit te verminderen en de endogene synthese van glucose te vertragen. De werking ervan verhoogt de insulinesecretie en stimuleert ook de glycolyse.
De therapeutische dosis die in de meeste klinische studies wordt gebruikt, is 200 tot 500 mg, 2 tot 3 keer per dag. In dit supplement wordt berberine aangeboden in de vorm van een plantaardige capsule van 500 mg, in te nemen net voor de maaltijden, volgens dezelfde periodiciteit.
Net als medicijnen varieert de werking van voedingssupplementen afhankelijk van het organisme van elk individu, de levensstijl, enz. Daarom is het toch belangrijk om een gezondheidsprofessional te raadplegen voordat u deze supplementen inneemt, vooral als er tegelijkertijd medicamenteuze behandelingen worden gebruikt.
Met vriendelijke groet,
Gaëlle - Supersmart
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
8 juni- 2020
Ce produit me réussit
Dit product bevalt me goed
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 juni- 2020
30 mei 2020
BON PRODUIT QUI A PERMIS DE SUPPRIMER METFORMINE (problème de diarrhée)
GOED PRODUCT DAT HET MOGELIJK MAAKTE OM METFORMINE TE STOPPEN (diarreeprobleem)
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
25 mei 2020
Je le prends depuis plusieurs mois et il est efficace,mon diabète est équilibré.
Ik neem het al enkele maanden en het is effectief, mijn diabetes is onder controle.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 mei 2020
Muy satisfecha con el producto.
Zeer tevreden met het product.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
8 april 2020
Ein gutes Produkt mit sauberer Zusammensetzung. Wir nehmen es bei Diabetes und Brustkrebsnachsorge. Der Preis ist für mich nicht ausschlaggebend, da ich seit Jahren bei Supersmart bestelle und einen erheblichen Preisnachlass habe.
Een goed product met een schone samenstelling. We gebruiken het bij diabetes en nazorg na borstkanker. De prijs is voor mij niet doorslaggevend, omdat ik al jaren bij Supersmart bestel en een aanzienlijke korting heb.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
8 april 2020
me permet de contrôler ma glycémie
stelt me in staat mijn bloedsuikerspiegel te controleren
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 maart 2020
prévention du diabète gras sans les effets secondaires de certains médicaments hypoglycémiants
preventie van vetdiabetes zonder de bijwerkingen van sommige bloedsuikerverlagende medicijnen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
27 maart 2020
18 maart 2020
Trés bon produit, c'est u peu cher mais quand on en prend plusieurs, il ya une remise quantitative. à recommender.
Zeer goed product, het is een beetje duur maar als je er meerdere neemt, is er een kwantumkorting. Aanbevolen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
17 maart 2020
Je l’utilise depuis des mois
Ik gebruik het al maanden
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 maart 2020
Inconvenient: Constipation, je suis oblige d arreter la prise de berberine : C est dommage. Sinon pour faire baisser le taux sucre ca reste un bon complement mais avec du sport.
Onaangenaam: Constipatie, ik ben genoodzaakt om te stoppen met het innemen van berberine: Het is jammer. Anders is het een goed supplement om de bloedsuikerspiegel te verlagen, maar wel met sport.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
13 maart 2020
Plante très intéressante. Pour les diabétiques notamment. Mais plus encore ...
Zeer interessante plant. Vooral voor diabetici. Maar nog meer ...
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
10 maart 2020
23 februari 2020
Util como complemento para control glucosa y colesterol.
Handig als supplement voor het beheersen van glucose en cholesterol.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
17 februari 2020
A pesar de los cuidados en alimentación evitando los hidratos de carbono y azúcares sigo con el nivel de azúcar un poco alto.
Ondanks de zorg voor voeding waarbij koolhydraten en suikers worden vermeden, blijft mijn suikergehalte nog steeds een beetje hoog.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 februari 2020
évite des produits chimiques nocifs, pour un résultat identique
vermijdt schadelijke chemicaliën, voor hetzelfde resultaat
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
14 februari 2020
je ne me pose pas de questions sur la qualité du produit que supersmart propose je me pose des questions sur l'efficacité de la berbérine en général: je prends ce produit pour réguler mon taux de glycémie et parfois il me semble que la berbérine que l'on me vend n' a pas trop d'effet...
Ik heb geen twijfels over de kwaliteit van het product dat Supersmart aanbiedt, maar ik heb vragen over de effectiviteit van berberine in het algemeen: ik neem dit product om mijn bloedsuikerspiegel te reguleren en soms lijkt het erop dat de berberine die ik koop niet veel effect heeft...
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
14 februari 2020
Tous les produits me conviennent donc je les commande régulièrement
Alle producten bevallen me, dus ik bestel ze regelmatig.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
10 februari 2020
MIEUX QUE LA METFORMINE
BETER DAN METFORMINE
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 februari 2020
2 februari 2020
Je préférai les comprîmes qui étaient plus efficaces que les gélules sans changement j’ai vu mon Hbg et ma glycémie à jeun augmenter alors à quand le retour aux comprimés ?
Ik gaf de voorkeur aan de tabletten die effectiever waren dan de capsules. Zonder verandering zag ik mijn HbA1c en mijn nuchtere bloedsuiker stijgen. Wanneer komen de tabletten terug?
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
2 februari 2020
RAS ça fonctionne pour moi
Geen bijzonderheden, het werkt voor mij
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
2 februari 2020
31 Januari 2020
Je prend depuis longtemps et je suis très satisfait
Ik gebruik het al lange tijd en ik ben zeer tevreden
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
21 Januari 2020
très bon produit pour les diabétiques, diminue naturellement la glycémie
Zeer goed product voor diabetici, verlaagt de bloedsuikerspiegel op natuurlijke wijze
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
20 Januari 2020
20 Januari 2020
Me parece un buen producto
Ik vind het een goed product
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 Januari 2020
19 Januari 2020
Resultat sur paramètres biologiques
Resultaat op biologische parameters
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 Januari 2020
Cumple con lo que promete
Voldoet aan wat het belooft
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
15 Januari 2020
Très bon produit et pour moi très efficaces
Zeer goed product en voor mij zeer effectief
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
13 Januari 2020
Bon produit,mais un peu cher !!
Goed product, maar een beetje duur!!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 Januari 2020
semble efficace...
lijkt effectief...
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
27 december 2019
18 december 2019
Diabétique, grâce à ce produit que je prends depuis environ deux ans, j'arrive à maintenir mon taux de glycémie à un taux raisonnable avec un régime sans sucres associés, sans avoir besoin de recourir aux médicaments traditionnellement prescrits.
Diabeetpatiënt, dankzij dit product dat ik al ongeveer twee jaar gebruik, slaag ik erin mijn bloedsuikerspiegel op een redelijk niveau te houden met een dieet zonder toegevoegde suikers, zonder dat ik de traditioneel voorgeschreven medicijnen nodig heb.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 december 2019
Bon produit et efficace ma glycémie a baissée.
Goed product en effectief, mijn bloedsuikerspiegel is gedaald.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
17 december 2019
Mon mari utilise la berbérine depuis trois ans contre une hyperglycémie. Les analyses, qui s'étaient révélées à l'époque assez inquiétantes, sont bien meilleures et nous échappons pour le moment à la médication traditionnelle (metformine) et à ses effets secondaires. Aucun problème jusqu'ici avec la berbérine.
Mijn man gebruikt al drie jaar berberine tegen een te hoge bloedsuikerspiegel. De analyses, die destijds behoorlijk zorgwekkend waren, zijn veel beter en we ontkomen voorlopig aan de traditionele medicatie (metformine) en de bijwerkingen daarvan. Tot nu toe geen problemen met berberine.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 december 2019
Produit très efficace. J'ai 75 ans et je pèse 90 kg pour 1.82 mètres. Je l'utilise en complément de médicaments chimiques (metformine) pour soigner un diabète de type 2 . Depuis que j'utilise la berbérine (3 gélules par jour) mon taux d'hémoglobine glyquée et stabilisé à 6.5% sans suivre de régime alimentaire particulier..
Zeer effectief product. Ik ben 75 jaar en weeg 90 kg bij een lengte van 1,82 meter. Ik gebruik het als aanvulling op chemische medicijnen (metformine) om type 2 diabetes te behandelen. Sinds ik berberine gebruik (3 capsules per dag) is mijn geglyceerde hemoglobine gestabiliseerd op 6,5% zonder een specifiek dieet te volgen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
15 december 2019
12 december 2019
Bon produit mais cher suivant posologie
Goed product maar duur afhankelijk van de dosering
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
8 december 2019
Buen sustituto de la medicina química
Goed alternatief voor chemische medicijnen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 december 2019
bonjour se produit et super ils ma débarrasser de tous mes problèmes gastrique a aussi éliminer les douleur quand je sorter de la selle et améliores mon cardiovasculaire ma vie serais plus longues .super
Hallo, dit product is geweldig. Het heeft me van al mijn maagproblemen afgeholpen, ook de pijn bij het ontlasten geëlimineerd en mijn cardiovasculaire gezondheid verbeterd. Mijn leven zal langer zijn. Super.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 december 2019
Très bon produit pour le diabète !
Zeer goed product voor diabetes!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 december 2019
Producto muy efectivo.
Zeer effectief product.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 december 2019
excellent produit pour diabetiques qui permet de prendre moins (voire supprimer) de medicaments allopathiques
uitstekend product voor diabetici dat het mogelijk maakt om minder (of zelfs geen) allopathische medicijnen te gebruiken
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 december 2019
our treatment is giving good results
onze behandeling geeft goede resultaten
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
29 november 2019
Super bei Diabetes Typ 2
Super bij diabetes type 2
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
26 november 2019
Funciona bien para mantener a raya la enfermedad, es para lo que está creado.
Het werkt goed om de ziekte onder controle te houden, dat is waar het voor is gemaakt.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
24 november 2019
23 november 2019
Muy contento con Berberine, la cual me sirve para controlar mi glucemia.
Zeer tevreden met Berberine, die me helpt mijn bloedsuikerspiegel onder controle te houden.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
22 november 2019
Super produit pas d'effets secondaires et très efficaces Je le recommande
Super product, geen bijwerkingen en zeer effectief. Ik beveel het aan.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
21 november 2019
Produto de óptima qualidade. Recomendado.
Product van uitstekende kwaliteit. Aanbevolen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 november 2019
Berberine est très efficace il fait bien baisser ma glycémie je ne prend plus de netphormine
Berberine is zeer effectief, het verlaagt mijn bloedsuikerspiegel goed, ik neem geen netformine meer.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
13 november 2019
J’aime beaucoup ce produit
Ik vind dit product erg goed
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
10 november 2019
Tres satisfait de ce produit qui me permet de mieux reguler mon diabete
Zeer tevreden over dit product dat me helpt mijn diabetes beter te reguleren
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
7 november 2019
Remplace totalement la Metformine sans les inconvénients !
Vervangt volledig Metformine zonder de nadelen!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 november 2019
Très bon produit en cas de diabète 2, une bonne et efficace alternative à la Metformine
Zeer goed product bij diabetes type 2, een goed en effectief alternatief voor Metformine
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 oktober 2019
bonjour je suis de la reunion un petit ile perdue au milieux de l'ocean indien un bo jour j'ai découvert par hassart en cherchant un remède naturel pour mon diabète sur le net et je suis tombé sur la berberine : bien qua la reunion on en a pas mal de remède de grand mère a base de plantes j'avais envie' de l'essayer donc j'ai commandé une reserve de berberine quant j'ai réceptionne ce produit j'ai mi de coté tout le fameux pilule qui cause pas mal effet secondaire je me suis mis au berberine tout en ajustant la dose en fonctions de la demande et le résultat a été très satisfaisant et au final j'ai tout mis les medicament chimique a la poubel et je me porte très bien ( mais pour arrivé a ce résultat tout ce qui dit mal bouffe fait une + mais bien sur ce conseille ne regarde que moi mais si vous avez envie de l'essayé essayer le berberine et vous verré bien salutations un utilisateur des produit bio
Hallo, ik ben van Réunion, een klein eiland verloren in het midden van de Indische Oceaan. Op een mooie dag ontdekte ik toevallig, terwijl ik op het internet naar een natuurlijke remedie voor mijn diabetes zocht, berberine. Hoewel we op Réunion veel grootmoedersremedies op basis van planten hebben, wilde ik het proberen. Dus bestelde ik een voorraad berberine. Toen ik dit product ontving, zette ik alle bekende pillen die veel bijwerkingen veroorzaken opzij. Ik begon met berberine en paste de dosis aan op basis van de behoefte. Het resultaat was zeer bevredigend en uiteindelijk heb ik alle chemische medicijnen weggegooid en voel ik me heel goed. (Maar om dit resultaat te bereiken, moet je ook slechte voeding vermijden, maar natuurlijk is dit advies alleen voor mij. Als je het wilt proberen, probeer dan berberine en je zult zien. Groeten, een gebruiker van biologische producten.)
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
13 oktober 2019
Super… très bon paliatif à la medformine...
Super... zeer goed alternatief voor metformine...
Nous sommes ravis d'avoir pu vous satisfaire, merci de ce partage.
Bien à vous,
Gaëlle – Supersmart
We zijn blij dat we u tevreden hebben kunnen stellen, bedankt voor het delen.
Met vriendelijke groet,
Gaëlle – Supersmart
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
10 oktober 2019
J'obtiens d'excellent résultat avec mes hyperglycémies.
Ik behaal uitstekende resultaten met mijn hyperglycemieën.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 september 2019
très bon résultat lors des analyses de sang
zeer goed resultaat bij bloedonderzoek
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
22 september 2019
20 september 2019
Les prix ne sont pas à la porté de tout le monde.
De prijzen zijn niet voor iedereen betaalbaar.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 september 2019
11 september 2019
Produits un peu cher mais je le prends pour le foie je m’en trouve bien
Producten zijn een beetje duur, maar ik neem het voor mijn lever en ik voel me er goed bij.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
13 augustus 2019
Equivaut à de la Metformine, sans les effets indésirables. Très bonne tolérance digestive. Très bon rapport qualité/ prix
Komt overeen met metformine, zonder de bijwerkingen. Zeer goede spijsverteringstolerantie. Zeer goede prijs-kwaliteitverhouding
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 augustus 2019
7 augustus 2019
Je renouvelle mes commandes donc RAS
Ik vernieuw mijn bestellingen dus NVT
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
3 augustus 2019
31 juli- 2019
gfhgfbhdgfbdfbcgf
gfhgfbhdgfbdfbcgf
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
27 juli- 2019
remplace le metformine sans effets secondaires
vervangt metformine zonder bijwerkingen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
27 juli- 2019
probablement utile
waarschijnlijk nuttig
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
26 juli- 2019
Ce produit m’a fait beaucoup de bien
Dit product heeft me veel goed gedaan
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
22 juli- 2019
Utilisé avec efficacité pour faire baisser la glycémie.
Effectief gebruikt om de bloedsuikerspiegel te verlagen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
21 juli- 2019
PRODUIT INTERESSANT POUR LE DIABETE MAIS PAS SEUL
INTERESSANT PRODUCT VOOR DIABETES MAAR NIET ALLEEN
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 juli- 2019
Produit correspond à mes attentes.
Product voldoet aan mijn verwachtingen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
14 juli- 2019
Muy buen producto
Zeer goed product
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
10 juli- 2019
Prix onéreux par rapport aux laboratoires concurrents Pas d information sur la présence de pesticides
Hoge prijs in vergelijking met concurrerende laboratoria Geen informatie over de aanwezigheid van pesticiden
Bonjour,
Lorsque Supersmart.com conçoit un produit, ni le prix de revient ni le prix de vente n’entrent en ligne de compte. Nous utilisons les ingrédients mêmes qui sont validés dans les études scientifiques, sous la même forme et aux mêmes dosages. Nous les conditionnons ensuite pour obtenir la meilleure biodisponibilité. Nous appliquons enfin des marges qui sont le standard dans notre industrie, ni plus ni moins, et le prix de vente ne fait l’objet d’aucune manipulation. Si un produit Supersmart.com est parfois plus cher, en apparence, qu’un autre produit européen, c’est uniquement en raison de critères de qualité plus élevés. Et l’avantageux programme de fidélisation dont bénéficient nos clients fait beaucoup plus que compenser cet éventuel désavantage. Par contre, nous admettons volontiers que les prix des suppléments nutritionnels européens sont supérieurs à ceux des produits similaires vendus aux États-Unis. Le marché américain de la supplémentation est le plus important au monde et les conditions fiscales et réglementaires auxquelles sont soumises les entreprises y sont incomparablement plus favorables. D’où des prix américains plus bas.
Si vous souhaitez plus de renseignements sur nos produits, vous pouvez faire la demande simplement par téléphone ou par email, nos conseillères se feront un réel plaisir de vous apporter les éléments manquants.
Bien à vous,
Gaëlle - Supersmart
Hallo,
Wanneer Supersmart.com een product ontwerpt, worden noch de kostprijs noch de verkoopprijs in overweging genomen. We gebruiken dezelfde ingrediënten die in wetenschappelijke studies zijn gevalideerd, in dezelfde vorm en doseringen. We verpakken ze vervolgens om de beste biologische beschikbaarheid te verkrijgen. Ten slotte passen we marges toe die de standaard zijn in onze industrie, niet meer en niet minder, en de verkoopprijs wordt op geen enkele manier gemanipuleerd. Als een product van Supersmart.com soms duurder lijkt dan een ander Europees product, is dat uitsluitend vanwege hogere kwaliteitscriteria. En het voordelige loyaliteitsprogramma waar onze klanten van profiteren, compenseert dit eventuele nadeel ruimschoots. We geven echter graag toe dat de prijzen van Europese voedingssupplementen hoger zijn dan die van vergelijkbare producten die in de Verenigde Staten worden verkocht. De Amerikaanse supplementenmarkt is de grootste ter wereld en de fiscale en regelgevende voorwaarden waaraan bedrijven daar zijn onderworpen, zijn onvergelijkbaar gunstiger. Vandaar de lagere Amerikaanse prijzen.
Als u meer informatie wilt over onze producten, kunt u eenvoudig telefonisch of per e-mail een aanvraag indienen, onze adviseurs helpen u graag met de ontbrekende elementen.
Met vriendelijke groet,
Gaëlle - Supersmart
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 juli- 2019
J'en ai pris un moment, ça fonctionne.
Ik heb het een tijdje genomen, het werkt.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 juni- 2019
Creo que es un producto innovador contra la Diabetes y por eso lo tomo
Ik denk dat het een innovatief product tegen diabetes is en daarom neem ik het.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 juni- 2019
Bon produit, un peu cher sur une prise à long terme.
Goed product, een beetje duur bij langdurig gebruik.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
15 juni- 2019
14 juni- 2019
pas de problème avec ce produit, pour mon diabète 2
geen probleem met dit product, voor mijn diabetes type 2
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
12 juni- 2019
Les gélules sont faciles à avaler et elles n'ont pas de goût et ne donne pas de mauvaise sensation aux intestins j'ai perdu 15kilos je n'ai plus envie de sucre !
De capsules zijn gemakkelijk door te slikken en ze hebben geen smaak en geven geen vervelend gevoel in de darmen. Ik ben 15 kilo afgevallen en heb geen trek meer in suiker!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
10 juni- 2019
Plus que satisfaisant.
Meer dan bevredigend.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
2 juni- 2019
Semble être efficace
Lijkt effectief te zijn
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 mei 2019
bon remède pour diabétique
goed middel voor diabetici
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 mei 2019
à prendre régulièrement si on veut du résultat
regelmatig innemen als je resultaat wilt
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
15 mei 2019
bon produit qui agit bien
goed product dat goed werkt
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 mei 2019
c'est un excellent produit que ma femme et moi prenons depuis un certain temps
Het is een uitstekend product dat mijn vrouw en ik al een tijdje gebruiken.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
8 mei 2019
je ne peu pas dire grand chose pour le moment je dois faire une prise sang bientôt
ik kan op dit moment niet veel zeggen, ik moet binnenkort bloed laten prikken
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 mei 2019
Excellent comme complément voir substitut aux médicaments contre le diabète de type 2
Uitstekend als aanvulling of zelfs vervanging voor medicijnen tegen type 2 diabetes
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
4 mei 2019
Baja significativamente el nivel de Lípidos en sangre( colesterol y triglicéridos), el de glucosa no es tan claro
Verlaagt significant het niveau van lipiden in het bloed (cholesterol en triglyceriden), het effect op glucose is minder duidelijk.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
17 april 2019
Très bon produit, très bon résultat Merci
Zeer goed product, zeer goed resultaat Bedankt
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
15 april 2019
Ce produit salutaire pour les diabétiques n'est pas en vente libre en France. Pourtant il y en a des diabétiques...qui savent ou pas qu'ils le sont...
Dit heilzame product voor diabetici is niet vrij verkrijgbaar in Frankrijk. Toch zijn er diabetici... die weten of niet weten dat ze het zijn...
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
15 april 2019
Efficace à condition de suivre un régime alimentaire approprié et de faire du sport/des exercices physiques tous les jours. Je recommande.
Effectief op voorwaarde dat je een geschikt dieet volgt en elke dag sport/lichamelijke oefeningen doet. Ik raad het aan.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
12 april 2019
Sans effets secondaire, depuis trois ans que mon mari à découvert ce produit son diabète est équilibré, encore Bravo et merci
Zonder bijwerkingen, sinds drie jaar dat mijn man dit product heeft ontdekt is zijn diabetes in balans, nogmaals Bravo en bedankt
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 april 2019
anti diabétique ecvellent
antidiabetisch uitstekend
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 april 2019
Très efficace pour retirer le sucre dans le sang. Les analyses le prouvent.
Zeer effectief om suiker uit het bloed te verwijderen. De analyses bewijzen het.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
3 april 2019
Bon produit très très cher !
Goed product, maar erg duur!
Bonjour,
Nous sommes ravis que le produit vous apporte satisfaction.
Lorsque Supersmart.com conçoit un produit, ni le prix de revient ni le prix de vente n’entrent en ligne de compte. Nous utilisons les ingrédients mêmes qui sont validés dans les études scientifiques, sous la même forme et aux mêmes dosages. Nous les conditionnons ensuite pour obtenir la meilleure biodisponibilité. Nous appliquons enfin des marges qui sont le standard dans notre industrie, ni plus ni moins, et le prix de vente ne fait l’objet d’aucune manipulation. Si un produit Supersmart.com est parfois plus cher, en apparence, qu’un autre produit européen, c’est uniquement en raison de critères de qualité plus élevés. Et l’avantageux programme de fidélisation dont bénéficient nos clients fait beaucoup plus que compenser cet éventuel désavantage. Par contre, nous admettons volontiers que les prix des suppléments nutritionnels européens sont supérieurs à ceux des produits similaires vendus aux États-Unis. Le marché américain de la supplémentation est le plus important au monde et les conditions fiscales et réglementaires auxquelles sont soumises les entreprises y sont incomparablement plus favorables. D’où des prix américains plus bas.
Bien à vous,
Gaëlle - Supersmart
Hallo,
We zijn blij dat het product u tevredenheid brengt.
Wanneer Supersmart.com een product ontwerpt, worden noch de kostprijs noch de verkoopprijs in overweging genomen. We gebruiken dezelfde ingrediënten die in wetenschappelijke studies zijn gevalideerd, in dezelfde vorm en doseringen. We verpakken ze vervolgens om de beste biologische beschikbaarheid te verkrijgen. Ten slotte passen we marges toe die de standaard zijn in onze industrie, niet meer en niet minder, en de verkoopprijs wordt op geen enkele manier gemanipuleerd. Als een product van Supersmart.com soms duurder lijkt dan een ander Europees product, is dat uitsluitend vanwege hogere kwaliteitscriteria. En het voordelige loyaliteitsprogramma waar onze klanten van profiteren, compenseert dit eventuele nadeel ruimschoots. We geven echter graag toe dat de prijzen van Europese voedingssupplementen hoger zijn dan die van vergelijkbare producten die in de Verenigde Staten worden verkocht. De Amerikaanse markt voor supplementen is de grootste ter wereld en de fiscale en regelgevende voorwaarden waaraan bedrijven daar zijn onderworpen, zijn onvergelijkbaar gunstiger. Vandaar de lagere Amerikaanse prijzen.
Met vriendelijke groet,
Gaëlle - Supersmart
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 april 2019
Excellent produit
Uitstekend product
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 maart 2019
Très satisfaite et la plus pure du marché !!
Zeer tevreden en de puurste op de markt!!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 maart 2019
efficace pour réguler le diabéte
effectief voor het reguleren van diabetes
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
29 maart 2019
Très bon produit. J'ai essayé une autre marque rien à voir je suis revenu sur BERBERINE de chez Super Smart qui me convient parfaitement je recommande++++
Zeer goed product. Ik heb een ander merk geprobeerd, maar dat was niet vergelijkbaar. Ik ben teruggekomen op BERBERINE van Super Smart, die perfect bij me past. Ik beveel het ten zeerste aan++++
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
25 maart 2019
La berberine me donne mal aux intestins
Berberine geeft me darmklachten
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 maart 2019
Les résultats ont été ceux attendus
De resultaten waren zoals verwacht
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
21 maart 2019
très bon produit pour le diabète
erg goed product voor diabetes
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
12 maart 2019
ça fait 3 mois que je prends Berberine, et je n'aie aucune améloioration sur mon diabète ??????
Het is nu 3 maanden dat ik Berberine neem, en ik zie geen enkele verbetering in mijn diabetes ??????
Bonjour Mme BONNAUD,
Nous sommes navrés d'apprendre que Berberine n'a pas l'effet escompté sur votre pathologie.
Le diabète résulte de la combinaison de facteurs génétiques et environnementaux, ainsi que de facteurs liés au mode de vie. En général, chaque personne porte un bagage héréditaire qui la prédispose à souffrir de diabète ou au contraire la protège. Les chercheurs connaissent aujourd’hui plusieurs gènes qui rendent un individu à risque de développer un diabète de type 2. Chez les personnes génétiquement prédisposées à la maladie, c’est généralement le surpoids et particulièrement l’accumulation de gras dans les organes de l’abdomen qui entraînent une résistance à l’insuline, le premier pas vers le diabète de type 2.
Initialement, pour compenser la résistance à l’insuline, le pancréas se met à produire davantage d’insuline. Cependant, avec le temps, le pancréas s’épuise et la sécrétion d’insuline diminue. Il y a donc un manque relatif d’insuline et la glycémie reste alors élevée de façon continue.
Le diabète de type 2 est donc le résultat de 2 phénomènes : d’abord une résistance à l’insuline, ensuite l’épuisement du pancréas.
Sachant cela, nous préconisons un rééquilibrage alimentaire associé à la prise de Berberine et/ou Metformine ainsi que la pratique d'une activité sportive, tel qu'une marche quotidienne d'au moins 45 mn.
Je vous invite à joindre l'une de nos conseillère afin qu'elle puisse vous apporter les explications nécessaires.
Bien à vous,
Gaëlle - Supersmart
Hallo mevrouw BONNAUD,
Het spijt ons te horen dat Berberine niet het gewenste effect heeft op uw aandoening. Diabetes is het resultaat van een combinatie van genetische en omgevingsfactoren, evenals factoren die verband houden met de levensstijl. Over het algemeen draagt elke persoon een erfelijke bagage die hem of haar vatbaar maakt voor diabetes of juist beschermt. Onderzoekers kennen tegenwoordig verschillende genen die een individu een risico geven om type 2 diabetes te ontwikkelen. Bij mensen die genetisch vatbaar zijn voor de ziekte, is het meestal overgewicht en vooral de ophoping van vet in de organen van de buik die insulineresistentie veroorzaakt, de eerste stap naar type 2 diabetes.
Aanvankelijk, om de insulineresistentie te compenseren, begint de alvleesklier meer insuline te produceren. Echter, na verloop van tijd raakt de alvleesklier uitgeput en neemt de insulinesecretie af. Er is dus een relatief tekort aan insuline en de bloedsuikerspiegel blijft dan continu hoog.
Type 2 diabetes is dus het resultaat van 2 verschijnselen: eerst insulineresistentie, daarna uitputting van de alvleesklier.
Gezien dit, raden wij een herziening van het dieet aan in combinatie met het gebruik van Berberine en/of Metformine, evenals het beoefenen van een sportieve activiteit, zoals een dagelijkse wandeling van minstens 45 minuten. Ik nodig u uit om contact op te nemen met een van onze adviseurs zodat zij u de nodige uitleg kan geven.
Met vriendelijke groet,
Gaëlle - Supersmart
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 maart 2019
Je suis diabétique, j'utilise de la BERBERINE, suite a un déménagement je suis resté sans durant 1 mois, mon taux de sucre est monté à 125 alors qu'il se situait entre 95 et 100 Michel TRAPPLER
Ik ben diabetisch, ik gebruik BERBERINE, na een verhuizing heb ik een maand zonder gezeten, mijn bloedsuikerspiegel steeg naar 125 terwijl deze tussen 95 en 100 lag Michel TRAPPLER
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 maart 2019
b produit a conseiller
b product aan te bevelen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
28 februari 2019
Pour moi ce produit ma changé la vie .je n’étais pas bien . Et en un mois je suis revenu capable de faire des actions que je ne pouvais plus réaliser
Voor mij heeft dit product mijn leven veranderd. Ik voelde me niet goed. En binnen een maand was ik weer in staat om dingen te doen die ik niet meer kon uitvoeren.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
27 februari 2019
Utilisé depuis plus d'un an, les effets sont lents mais progressifs.
Al meer dan een jaar gebruikt, de effecten zijn traag maar progressief.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
24 februari 2019
24 februari 2019
Rien à dire ça fonctionne pour moi .
Niets op aan te merken, het werkt voor mij.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 februari 2019
J'attends les résultats à 3 mois de mon hémoglobine glicquée.
Ik wacht op de resultaten van mijn geglyceerde hemoglobine over 3 maanden.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 februari 2019
Mantiene el azúcar a raya. Funciona.
Houdt de suiker onder controle. Het werkt.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 februari 2019
Remplace avantageusement la Metformine et n'a pas d'effets indésirables.Une formule très bien adaptée au diabète de type 2
Vervangt met voordeel Metformine en heeft geen bijwerkingen. Een zeer goed aangepaste formule voor type 2 diabetes.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 februari 2019
ES excelente para tratar la diabetes tipo 2
Het is uitstekend voor de behandeling van type 2 diabetes
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
17 februari 2019
Très efficace. Et surtout si ans effet secondaire comme.la.metformine.
Zeer effectief. En vooral zonder bijwerkingen zoals metformine.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 februari 2019
Bon produit qui semble donner de bon resultats
Goed product dat goede resultaten lijkt te geven
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 februari 2019
Bon produit alternatif
Goed alternatief product
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
22 Januari 2019
Das Produkt wirkt. Bei Diabetes Typ 2 liegt der gemessene Zuckerwert ca. 10 Punkte niedriger. Auch die Werte bzgl Fettstoffwechsel sind besser.
Het product werkt. Bij diabetes type 2 ligt de gemeten suikerwaarde ongeveer 10 punten lager. Ook de waarden met betrekking tot de vetstofwisseling zijn beter.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
20 Januari 2019
pour remplacer la metformine, je donne à mon mari de la berberine mais au bout de 6 mois, le résultat n'est pas encore satisfaisant
om metformine te vervangen, geef ik mijn man berberine, maar na 6 maanden is het resultaat nog steeds niet bevredigend
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 Januari 2019
Très bon produit,je l'utilise tous les jours !
Zeer goed product, ik gebruik het elke dag!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
3 december 2018
Excellent produit que je prescris et vends dans ma boutique Bio-Nat à mes patients diabétiques
Uitstekend product dat ik voorschrijf en verkoop in mijn Bio-Nat winkel aan mijn diabetespatiënten
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 november 2018
produit efficace dans mon cas ; mes niveaux de cholestérol, de triglycérides et de sucre ont baissé significativement
effectief product in mijn geval; mijn cholesterol-, triglyceriden- en suikerniveaus zijn aanzienlijk gedaald
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 oktober 2018
super efficace j'en ai modifié la prise de mes autre médicaments
super effectief, ik heb de inname van mijn andere medicijnen aangepast
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
22 oktober 2018
Les résultats annoncés sont là. Pas d' effets secondaires à ce jour.
De aangekondigde resultaten zijn er. Tot op heden geen bijwerkingen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 oktober 2018
Es necesario ser constante durante un periodo continuado y prolongado
Het is noodzakelijk om gedurende een langere en aaneengesloten periode consistent te zijn
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
7 oktober 2018
Muy buen producto. Lo volvería a comprar.
Zeer goed product. Ik zou het opnieuw kopen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 september 2018
Tout bien, tant au niveau commande que délais.
Alles goed, zowel wat betreft de bestelling als de levertijden.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
15 september 2018
Excellent produit qui a aidé une personne diabétique 2 de supprimer tout traitement allopathique (couplé avec une alimentation saine et exercicew physiques
Uitstekend product dat een persoon met diabetes type 2 heeft geholpen om alle allopathische behandelingen te stoppen (in combinatie met een gezond dieet en lichaamsbeweging).
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 september 2018
Lo he tomado en sustitución de Metformina que me recetaba mi doctor. No he notado ninguna contraindicación. Tampoco ninguna mejoría.
Ik heb het ingenomen ter vervanging van Metformine die mijn arts mij had voorgeschreven. Ik heb geen bijwerkingen opgemerkt. Ook geen verbetering.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 september 2018
le diabète a été maitrisé grâce à ce produit.les analyses le prouvent tous les trois mois.merci
diabetes is onder controle dankzij dit product. De analyses bewijzen het elke drie maanden. Bedankt
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 september 2018
Très bonne qualité et très efficace
Zeer goede kwaliteit en zeer effectief
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
16 augustus 2018
je recommande BERBERINE 500mg surtout pour le diabète mon mari en prends 1 avant chaque repas le résultat est spectaculaire très bon produit+++
Ik raad BERBERINE 500mg vooral aan voor diabetes. Mijn man neemt er één voor elke maaltijd en het resultaat is spectaculair. Zeer goed product+++
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
13 augustus 2018
tres bon produit .. et efficace
heel goed product .. en effectief
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
12 augustus 2018
je commande ce produit pour une amie atteinte d'un diabète type 2 , produit qui remplace très bien un produit prescrit en pharmacie dont je tairai le nom mais qui a des effets secondaire désagréables .
Ik bestel dit product voor een vriendin met type 2 diabetes. Dit product vervangt heel goed een voorgeschreven medicijn uit de apotheek, waarvan ik de naam niet zal noemen, maar dat onaangename bijwerkingen heeft.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 augustus 2018
La Berbérine fait VRAIMENT baisser (un peu) la glycémie. Produit efficace donc, mais cher !
Berberine verlaagt ECHT (een beetje) de bloedsuikerspiegel. Dus een effectief product, maar duur!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 augustus 2018
Merci Merci Merci Merci Merci Merci Merci Merci Merci Merci
Dank u Dank u Dank u Dank u Dank u Dank u Dank u Dank u Dank u Dank u
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
8 augustus 2018
Je viens de passer ma 3ème commande (pour 3 mois) : efficace dès le 1er trimestre pour faire baisser la glycémie...seul bémol : j'ai reçu des capsules pour mes 2 premières commandes et des gélules pour la 3ème commande....j'ai peut-être pas fait attention car c'était un renouvellement pour moi....mais plus facile à prendre que les comprimés donc...RAS
Ik heb net mijn derde bestelling geplaatst (voor 3 maanden): effectief vanaf het eerste trimester om de bloedsuikerspiegel te verlagen...enige minpunt: ik heb capsules ontvangen voor mijn eerste twee bestellingen en capsules voor de derde bestelling...misschien heb ik niet goed opgelet omdat het een hernieuwing voor mij was...maar gemakkelijker in te nemen dan tabletten dus...geen bijzonderheden.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
7 augustus 2018
surpprenant d'efficacit!Au vu ds analyses mo edecin a eu peur
verrassend effectief! Gezien de analyses was mijn arts bang
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
2 augustus 2018
Je ne fait que passer le message .la personne concernee est satisfaite du produit la preuve j en commande d une façon régulière.
Ik geef alleen de boodschap door. De betreffende persoon is tevreden met het product, het bewijs is dat ik het regelmatig bestel.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
29 juli- 2018
Aucun commentaire pour le moment. j'attends mes analyses de sang pour me faire une opinion. si cela est positif je continuerai à prendre Berberine. Si cela s'avère négatif je reprendrai Netformine
Nog geen commentaar op dit moment. Ik wacht op mijn bloedonderzoeken om een mening te vormen. Als het positief is, zal ik doorgaan met het nemen van Berberine. Als het negatief blijkt te zijn, zal ik weer Netformine nemen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
29 juli- 2018
Bon produit que j'utilise depuis plusieurs mois
Goed product dat ik al enkele maanden gebruik
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
28 juli- 2018
Très bon produit mais chere
Zeer goed product maar duur
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
24 juli- 2018
efficace j en ai la preuve pour le diabéte
effectief, ik heb het bewijs voor diabetes
Bonjour Mme ROUSSELET,
Merci beaucoup d'avoir pris du temps pour partager votre expérience.
Bonne journée,
Valérie - Supersmart
Hallo mevrouw ROUSSELET,
Hartelijk dank dat u de tijd heeft genomen om uw ervaring te delen.
Fijne dag,
Valérie - Supersmart
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
23 juli- 2018
Comme souvent, l'effet n'est pas immédiat mais sûr avec la berberine.
Zoals vaak is het effect niet onmiddellijk, maar wel zeker met berberine.
Bonjour Mme DARTIAL,
Merci de nous accorder votre confiance !
Bonne journée,
Valérie - Supersmart
Hallo mevrouw DARTIAL,
Bedankt voor uw vertrouwen!
Fijne dag,
Valérie - Supersmart
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
21 juli- 2018
Je préfère sous la forme gelule plutôt que sous la forme comprimé
Ik geef de voorkeur aan de capsulevorm boven de tabletvorm.
Bonjour,
Merci pour votre commentaire que je transmets à notre service achat.
Bonne journée,
Valérie – Supersmart
Hallo,
Bedankt voor uw opmerking die ik doorstuur naar onze inkoopafdeling.
Fijne dag,
Valérie – Supersmart
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
19 juli- 2018
Depuis des années je consomme la Berberine de Supersmart et continuerai sans aucun problème puisque je suis entièrement satisfait.
Al jaren gebruik ik de Berberine van Supersmart en ik zal zonder enige problemen doorgaan omdat ik volledig tevreden ben.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
18 juli- 2018
Changement de produit sans avertissement (passé de comprimés à gellules avec,d'après le descriptif la même composition ) et malgré le même régime alimentaire une petite augmentation de la glycémie
Productwijziging zonder waarschuwing (overgestapt van tabletten naar capsules met volgens de beschrijving dezelfde samenstelling) en ondanks hetzelfde dieet een kleine verhoging van de bloedsuikerspiegel.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
17 juli- 2018
très bon produit je le recommande à beaucoup de personnes
Zeer goed product, ik beveel het aan veel mensen aan
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
14 juli- 2018
Nous utilisons la berbérine pour réduire le taux de glycémie et pour nous ça marche.
Wij gebruiken berberine om de bloedsuikerspiegel te verlagen en voor ons werkt het.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
12 juli- 2018
Pour moi c'est un produit super car il me permet de faire baisser mon diabète de type 2 alors que tous les médicaments classiques n'avaient aucun effet avec plein d'effets secondaires notamment de l'hypoglycémie ..
Voor mij is dit een geweldig product omdat het me helpt mijn type 2 diabetes te verlagen, terwijl alle klassieke medicijnen geen effect hadden en veel bijwerkingen veroorzaakten, waaronder hypoglykemie.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
12 juli- 2018
Utilisée depuis plusieurs années, Remplace parfaitement la Metformine sans les effets nocifs.
Al jarenlang gebruikt, vervangt perfect Metformine zonder de schadelijke effecten.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 juli- 2018
Je peux recommander ce produit que j'ai pris en remplacement d'un produit allopathique qui n'a rien réglé pendant des années. Après 3 mois de prise de la Berbérine, tous les indicateurs de glycémie s'étaient améliorés d'après les résultats d'analyses. Les autres produits que je prends doivent être pris dans la durée et je n'ai pas fait d'analyses (si tant est qu'on puisse en faire) pouvant donner des résultats probants d'efficacité, sauf pour les oméga 3.
Ik kan dit product aanbevelen dat ik heb genomen ter vervanging van een allopathisch product dat jarenlang niets heeft opgelost. Na 3 maanden Berberine te hebben ingenomen, waren alle glykemie-indicatoren verbeterd volgens de analyseresultaten. De andere producten die ik neem, moeten langdurig worden ingenomen en ik heb geen analyses gedaan (als die al mogelijk zijn) die overtuigende resultaten van effectiviteit kunnen geven, behalve voor omega 3.
Bonjour,
Nous vous remercions pour ce commentaire et espérons continuer à vous satisfaire encore longtemps.
Bonne journée,
Valérie - Supersmart
Hallo,
Wij danken u voor deze opmerking en hopen u nog lang tevreden te kunnen stellen.
Fijne dag,
Valérie - Supersmart
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
11 juli- 2018
très bon produit donne des résultats satisfaisants je le recommande
Zeer goed product, geeft bevredigende resultaten, ik beveel het aan.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 juli- 2018
Je me sers de la berbérine pour soigner un diabète de type 2 avec succès et sans effets secondaires !
Ik gebruik berberine om type 2 diabetes met succes en zonder bijwerkingen te behandelen!
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
9 juli- 2018
les nouveaux comprimés sont moins efficaces que les anciens
de nieuwe tabletten zijn minder effectief dan de oude
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
8 juli- 2018
J'en commande depuis plusieurs mois,j'ai pu baisser les médicaments conventionnels et mon diabète est équilibré
Ik bestel het al enkele maanden, ik heb de conventionele medicijnen kunnen verminderen en mijn diabetes is in balans.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
6 juli- 2018
âgée de 75 ans diabète type 2, mon médecin à été très étonné lorsque je lui ai dit que c'était grâce à la Berberine que mon diabète était revenu au taux normal.
75 jaar oud, type 2 diabetes, mijn arts was zeer verbaasd toen ik hem vertelde dat het dankzij de Berberine was dat mijn diabetes weer op een normaal niveau was gekomen.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 juli- 2018
Nouveau Conditionnement en gélules...! pas annoncé, mais pourquoi pas ...?
Nieuwe verpakking in capsules...! niet aangekondigd, maar waarom niet ...?
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 juli- 2018
Dans ma deuxième boîte le contenu éta
In mijn tweede doos was de inhoud te
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
5 juli- 2018
Cela fait 3 ans que je consomme la Berberine et mon diabète a considérablement baissé, en parallèle avec une bonne hygiène alimentaire et de la marche régulière. Les médecins ont du mal à l'admettre mais quand ils voient mes résultats d'analyse ils ne peuvent que s'incliner. Je n'ai jamais ressenti d'effet secondaires, au contraire que des effets bénéfiques sur tout l'organisme, et plus d'infections urinaires. Je recommande vivement ce produit.
Het is nu 3 jaar dat ik Berberine gebruik en mijn diabetes is aanzienlijk verminderd, in combinatie met een goede voeding en regelmatig wandelen. De artsen hebben moeite om het toe te geven, maar als ze mijn testresultaten zien, kunnen ze niet anders dan buigen. Ik heb nooit bijwerkingen gevoeld, integendeel, alleen maar gunstige effecten op het hele lichaam, en geen urineweginfecties meer. Ik beveel dit product ten zeerste aan.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 juli- 2018
parfait conforme aux attentes
perfect in lijn met de verwachtingen
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 juli- 2018
Excellent - tout s'est très bien passé, je recommande vivement.
Uitstekend - alles is zeer goed verlopen, ik beveel het ten zeerste aan.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
1 juli- 2018
Traitement à apprécier sur un terme assez long, je n'ai pas encore le recul suffisant. La présentation en gélules facilite la prise par rapport aux comprimés (car la berberine est amère)
Behandeling om op lange termijn te waarderen, ik heb nog niet genoeg afstand om het volledig te beoordelen. De presentatie in capsules vergemakkelijkt de inname in vergelijking met tabletten (omdat berberine bitter is).
Bonjour Mr JUHENS,
Merci d'avoir pris le temps d'écrire et de partager votre expérience.
Désormais, vous retrouverez notre BERBERINE en gélules ce qui vous évitera d'avoir ce gout amer en bouche.
Merci de nous faire confiance.
Bonne journée,
Valérie - Supersmart
Hallo Mr. JUHENS,
Bedankt dat u de tijd heeft genomen om uw ervaring te schrijven en te delen.
Voortaan vindt u onze BERBERINE in capsules, zodat u die bittere smaak in uw mond niet meer heeft.
Bedankt voor uw vertrouwen.
Fijne dag,
Valérie - Supersmart
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 juni- 2018
Je commande ce produit pour ma mère pour remplacer les médocs anti-cholestérol en accord avec son médecin et ses analyses sont bonnes. Elle continue d'en prendre, ça fait juste cher à force car ce n'est pas remboursé...
Ik bestel dit product voor mijn moeder ter vervanging van cholesterolverlagende medicijnen in overleg met haar arts en haar analyses zijn goed. Ze blijft het gebruiken, maar het wordt op den duur wel duur omdat het niet wordt vergoed...
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
30 juni- 2018
Nos médecins ont proscrit ce produit pour conserver leurs malades diabétiques...2 comprimés par jour + un petit régime et mon diabète " tardif" de type 2 se tient bien dans les cordes. Merci Supersmart de distribuer ce produit qui devrait être en vente libre et remboursé par la sécu.
Onze artsen hebben dit product voorgeschreven om hun diabetespatiënten te helpen... 2 tabletten per dag + een klein dieet en mijn "late" type 2 diabetes blijft goed onder controle. Bedankt Supersmart voor het distribueren van dit product dat vrij verkrijgbaar en vergoed door de zorgverzekering zou moeten zijn.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
26 juni- 2018
Bonjour , j'utilise la Berberine depuis l'an dernier à raison pour l'instant un seul comprimé jour le matin, au petit déjeuner " excellent produit por moi .
Hallo, ik gebruik Berberine sinds vorig jaar, momenteel één tablet per dag 's ochtends bij het ontbijt. Uitstekend product voor mij.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
26 juni- 2018
La BERBERINE me permet de ne pas avaler des médicaments chimiques pour le même effet puisque mon diabète est parfaitement régulé.
De BERBERINE stelt me in staat om geen chemische medicijnen in te nemen voor hetzelfde effect, aangezien mijn diabetes perfect gereguleerd is.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
25 juni- 2018
Taux de triglycéride en baisse……………………….
Triglycerideniveau gedaald………………………
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
25 juni- 2018
Grâce à ce traitement, j'ai pu éviter de prendre un traitement chimique. Les résultats sont plutôt bons !
Dankzij deze behandeling heb ik kunnen vermijden een chemische behandeling te nemen. De resultaten zijn vrij goed!
Bonjour,
Nous sommes ravis de pouvoir vous apporter satisfaction et nous vous remercions de votre confiance.
Bonne journée,
Valérie – Supersmart
Hallo,
We zijn verheugd u tevreden te kunnen stellen en danken u voor uw vertrouwen.
Fijne dag,
Valérie – Supersmart
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
24 juni- 2018
J'attends de faire mon bilan sanguin pour savoir si mon taux de cholestérol a diminué. Les résultats se verront d ici trois mois car je viens de commencer le traitement. Je voulais faire un traitement le us naturel possible et je pense que la berberine est meilleure que les médicaments, les statines.
Ik wacht op mijn bloedonderzoek om te weten of mijn cholesterolgehalte is gedaald. De resultaten zullen over drie maanden zichtbaar zijn, omdat ik net met de behandeling ben begonnen. Ik wilde een zo natuurlijk mogelijke behandeling en ik denk dat berberine beter is dan medicijnen, statines.
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
24 juni- 2018
Après un mois d’utilisation mon taux de glycémie avait bien baissé. Je continue donc et nous verrons les prochains résultats.
Na een maand gebruik was mijn bloedsuikerspiegel aanzienlijk gedaald. Ik ga dus door en we zullen de volgende resultaten zien.
Bonjour Mme ACKERS,
Supersmart vous remercie pour cet avis.
Nous tenons à vous rappeler que l'efficacité des compléments nutritionnels tient dans la prise continue d'un minimum de 3 mois en respectant la posologie recommandée sur chaque produit.
Nos conseillères sont disponibles chaque jour entre 8h30 et 18h30 pour toutes questions complémentaires.
Cordialement,
Valérie - Supersmart
Hallo mevrouw ACKERS,
Supersmart bedankt u voor deze beoordeling.
Wij willen u eraan herinneren dat de effectiviteit van voedingssupplementen ligt in het continu innemen gedurende minimaal 3 maanden, met inachtneming van de aanbevolen dosering op elk product.
Onze adviseurs zijn elke dag beschikbaar tussen 8.30 en 18.30 uur voor aanvullende vragen.
Met vriendelijke groet,
Valérie - Supersmart
 zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
zie de vertaling
Vertaald door SuperSmart - bekijk het origineel
Hulp nodig?
Telefoon
Schrijf ons
Dit vindt u misschien ook interessant
geld terug




Berberine
Extract van Berberis vulgaris
Winteruitverkoop
Profiteer nu!













Buongiorno CATIA,
Grazie per il suo feedback molto positivo sulla Berberina. La sua soddisfazione è la nostra priorità e siamo lieti di sapere che apprezza i nostri prodotti e servizi.
Ci auguriamo di poter continuare ad accompagnarla a lungo nelle sue scelte di salute e benessere.
Con i nostri più sentiti ringraziamenti,
Il team Supersmart