Complete your selection
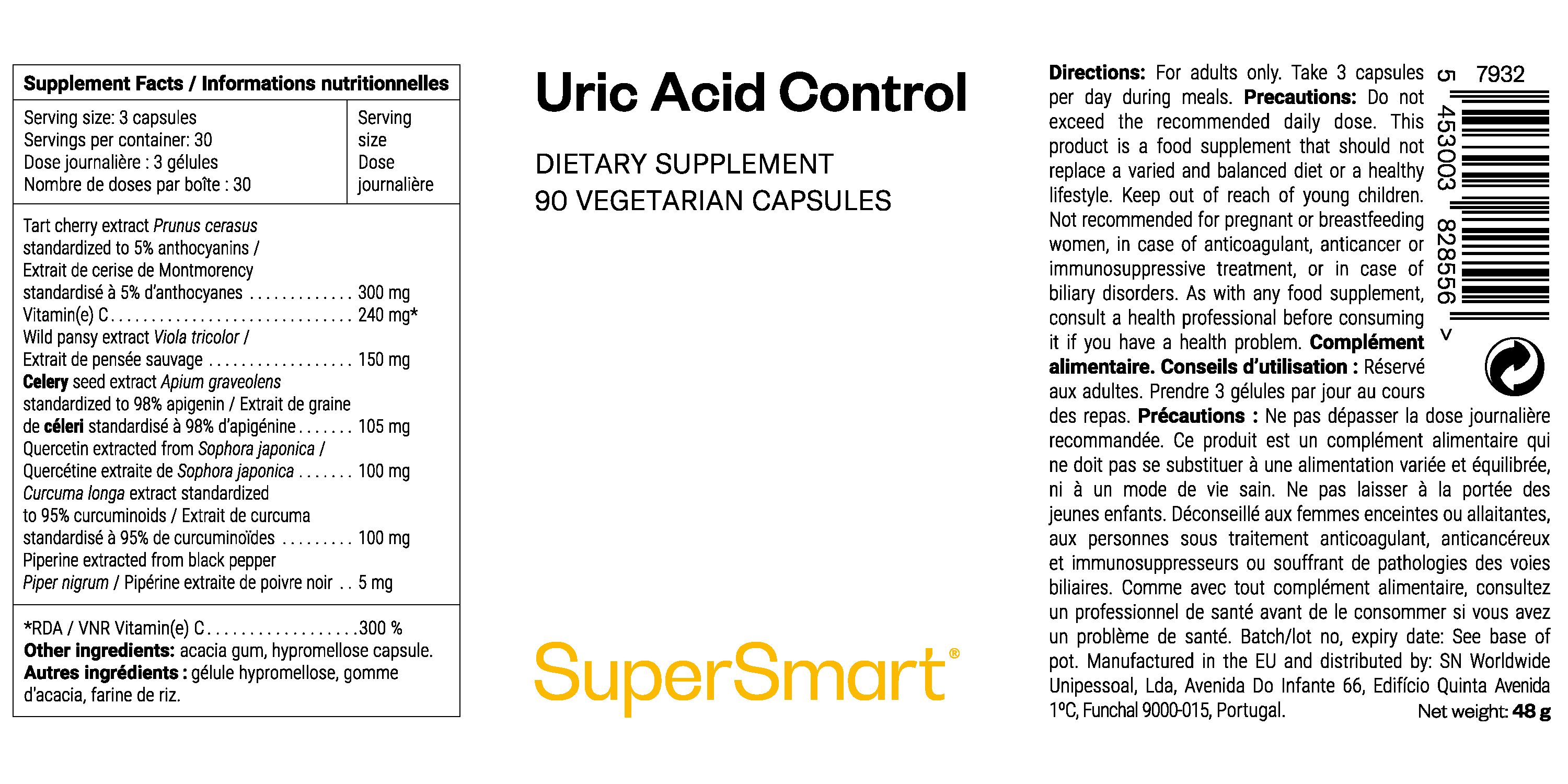
Uric Acid Control is a dietary supplement designed to regulate the level of uric acid, a metabolic waste product whose excess can lead to joint discomfort and metabolic imbalances.
This synergistic formula combines the best natural ingredients studied on this subject: wild pansy extract, potential inhibitors of xanthine oxidase (the enzyme which breaks down purines into uric acid), etc.
Uric Acid Control is in our category of products dedicated to maintaining inner balance.
Composition and benefits of our dietary supplement for lowering uric acid
Uric acid: definition and risks caused by hyperuricaemia
Uric acid is a nitrogenous waste product produced by the natural breakdown of purines, substances present in cells and certain foods.
Once filtered from the blood, mainly by the kidneys, uric acid is excreted in the urine.
When the balance between production and elimination is disturbed (due to overproduction of uric acid or reduced renal excretion), this metabolic waste product can accumulate in the blood, a condition known as hyperuricaemia.
Hyperuricaemia causes the formation of sharp urate crystals that deposit in the joints and trigger gout, a painful inflammatory arthritis.
Excess uric acid can be caused by certain metabolic disorders (obesity, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, etc.), which it can in turn aggravate.
Benefits of the 7 ingredients of Uric Acid Control
This dietary supplement has a triple action on uric acid levels: it inhibits production, facilitates elimination and soothes the effects on joints.
Specifically, it combines 7 carefully selected natural ingredients:
- extract of Montmorency cherry (Prunus cerasus) standardised to 5% anthocyanins: this tart cherry, with its rich nutritional content, is a fantastic source of flavonoids known as anthocyanins. Anthocyanins may increase renal elimination of uric acid and reduce the oxidative stress and inflammation associated with hyperuricaemia, which can accelerate joint complications. Montmorency cherries have also been studied in clinical trials to lower uric acid levels, with promising results (1-3);
- vitamin C: the most-well known vitamin is thought to have a uricosuric effect, i.e. the ability to improve the elimination of uric acid by the kidneys. A meta-analysis of 16 randomised trials, involving a total of 1,013 participants, highlights its possible effectiveness in reducing serum uric acid levels (4). Vitamin C also helps protect cells against oxidative stress and contributes to collagen formation, which is essential for the proper functioning of cartilage, a key factor in joint comfort and health;
- wild pansy extract (Viola tricolor): this medicinal plant has been recognised since the Middle Ages for its depurative and diuretic properties. It supports blood purification, normal diuresis (excretion of urine) and increased elimination of uric acid from the blood, via its flavonoids, saponins and potassium salts, which stimulate renal evacuation (5);
- extract of celery seed (Apium graveolens) standardised to 98% apigenin: celery seed is traditionally used as a spice and phytotherapeutic ingredient. Two flavonoids present in these seeds, apigenin and luteolin, are being studied for their potential ability to inhibit xanthine oxidase (XO), a key enzyme in the breakdown of purines (6). XO catalyses the oxidation of hypoxanthine to xanthine and then xanthine to uric acid. By binding to the enzyme's active site, the two flavonoids block its oxidative activity, resulting in a reduction in uric acid production;
- quercetin extracted from Sophora japonica: quercetin is a flavonoid found in onions, grapes and the ornamental tree Japanese Sophora, which contains it in larger quantities. It is also considered to be a possible natural inhibitor of xanthine oxidase, capable of occupying the active site of the enzyme to slow down its action (7);
- turmeric extract (Curcuma longa) standardised to 95% curcuminoids: turmeric is a condiment rich in curcumin, a polyphenol also studied for its potential ability to limit the activity of the xanthine oxidase enzyme by binding to its active site (8). Turmeric also supports the quality and production of blood, thanks to its role in stimulating collagen and protecting blood cells through its polyphenols. It helps to manage the inflammatory response by modulating certain signalling pathways such as NF-κB. It also contains natural antioxidants, including curcumin, which neutralise free radicals, thus helping to support joint health, flexibility and comfort, among other things;
- piperine extracted from black pepper (Piper nigrum): this bioactive compound is often added to synergistic formulas because it helps to increase the absorption and bioavailability of other nutrients, while providing its own antioxidant properties (9).
3 highlights of our natural formula designed to reduce excess uric acid
Uric Acid Control has 3 key strengths:
- a unique synergy of compounds backed by science: our formula contains the most effective ingredients ever combined to help regulate uric acid naturally. Their effects are systematically supported by the many studies, clinical trials and meta-analyses mentioned above;
- a triple targeted action, which is not limited to drainage: unlike most similar food supplements on the market, Uric Acid Control does not simply exert a draining action, but includes compounds specifically selected for their potential ability to reduce the production of uric acid, stimulate its elimination and repair its repercussions on the joints;
- a vegetable capsule with natural excipients: the capsules used are made from hypromellose (HPMC), a derivative of cellulose, the material contained in the membrane of plant cells. The only excipients in the formula are acacia gum and rice flour, two other plant compounds.
What is in Uric Acid Control
Any questions?
Our team of nutrition experts and scientists has the answers.
To eliminate excess uric acid from the body, you need to:
- drink plenty of water (1.5 to 2 litres a day) to support the kidneys in their excretory function;
- limit consumption of purine-rich foods (offal, red meat, seafood, alcohol);
- give preference to fruit, vegetables and light dairy products;
- maintain a healthy weight;
- practise regular physical activity;
- take advantage of natural compounds studied for this purpose, such as those found in Uric Acid Control.
Medical follow-up is necessary in the event of persistent high levels.
Because of its industrial fructose content, honey can increase the presence of uric acid and encourage the accumulation of crystals, thus contributing to the risk of gout and other kidney diseases.
So it's best to avoid excess honey, especially for people already prone to hyperuricaemia.
Moderate, occasional consumption is generally tolerated, but it is preferable to opt for other natural sources of sugar that are low in fructose, such as certain fresh fruits.
Several studies suggest that vitamin C has uricosuric properties: in other words, it helps to increase the elimination of uric acid through the urine, by promoting its excretion by the kidneys.
This could reduce the risk of hyperuricaemia, the main cause of gout attacks.
High levels of uric acid can lead to the formation of kidney stones. In addition to taking Uric Acid Control, fill up on natural ingredients that are good for kidney function (buy the Kidney Detox synergy formula, for example).
When it comes to joint health, consider the benefits of Boswellia serrata, the Ayurvedic plant from which frankincense is derived. Boswellia itself has been studied for its potential to reduce the formation of uric acid and is known to maintain good joint comfort by regulating inflammation (see Super Boswellia).
Finally, oxidative stress is a factor that can contribute to hyperuricaemia and encourage the accumulation of crystalline deposits. Take advantage of recognised compounds such as resveratrol, a powerful antioxidant that is particularly active and bioavailable in the form of trans-resveratrol (buy the complete Resveratrol Synergy formula, for example).
january 17 2026
Pas assez de recul dans l'utilisation
Not enough perspective in the use
 see the translation
Translated by SuperSmart - see the original
see the translation
Translated by SuperSmart - see the original
november 24 2025
gadget, préférez les tisanes sur d'autres sites
gadget, prefer herbal teas on other sites
 see the translation
Translated by SuperSmart - see the original
see the translation
Translated by SuperSmart - see the original
october 27 2025
Je n'ai pas assez de recul pour donner mon avis
I don't have enough perspective to give my opinion.
 see the translation
Translated by SuperSmart - see the original
see the translation
Translated by SuperSmart - see the original
Need help?
You may also like
of experience
your money back
##montant## purchase